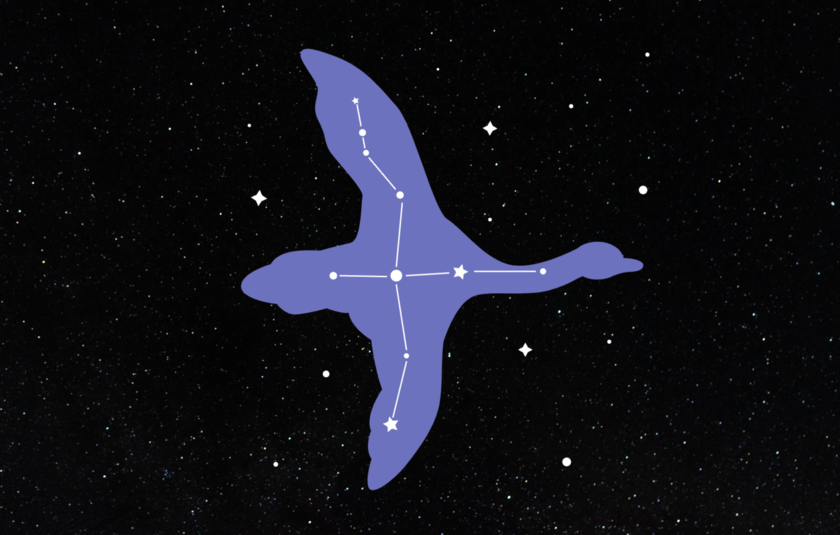
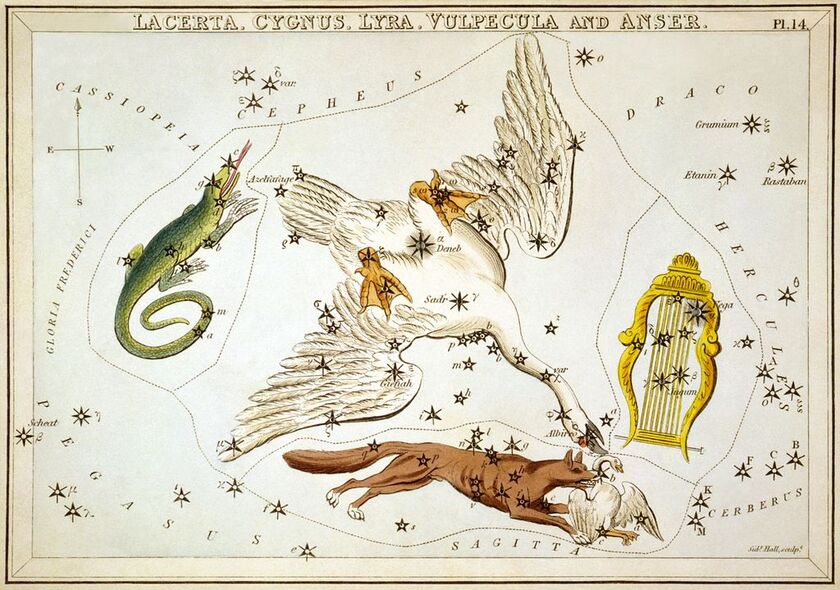
"The brightest star in the Cygnus constellation is Deneb, which is classified as an A-type supergiant. Deneb is one of the brightest stars visible from Earth, approximately 19 times more massive than the Sun, and shines 200,000 times brighter."
The Digital Package is ideal for those short on time. Register a star’s name and receive all documents via email in under 15 minutes, ready to download and print at home!