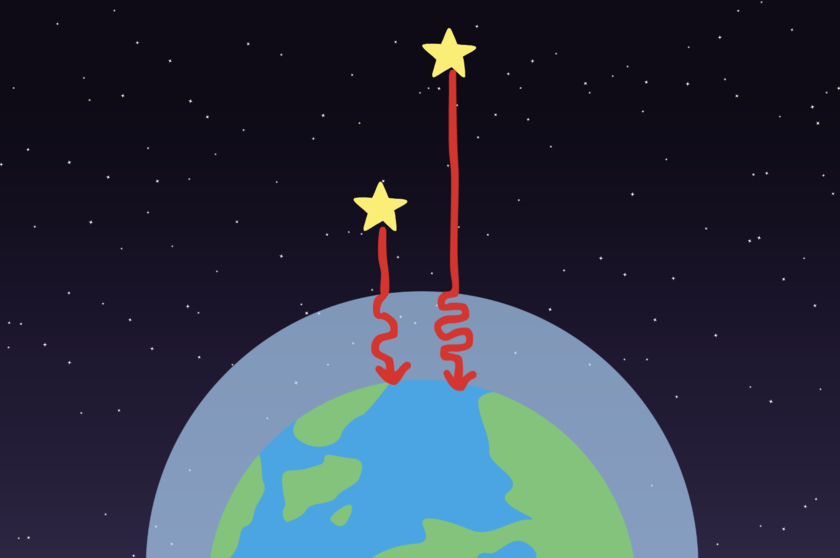
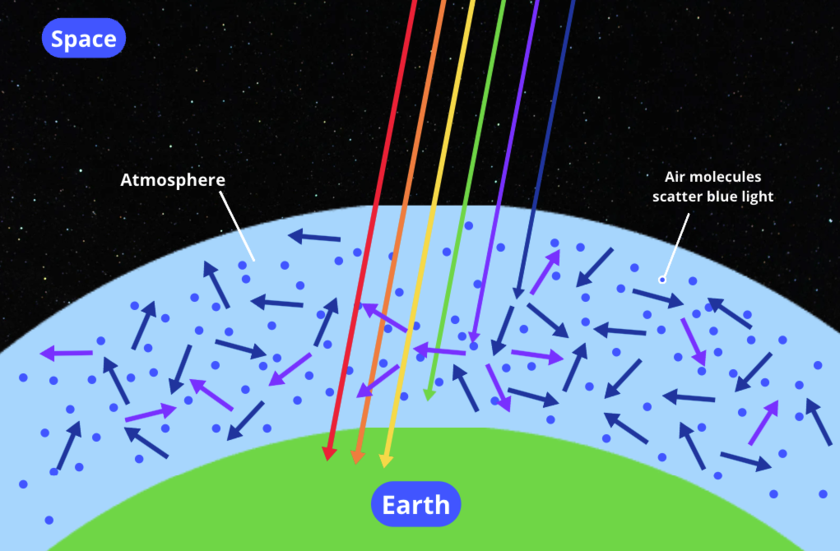
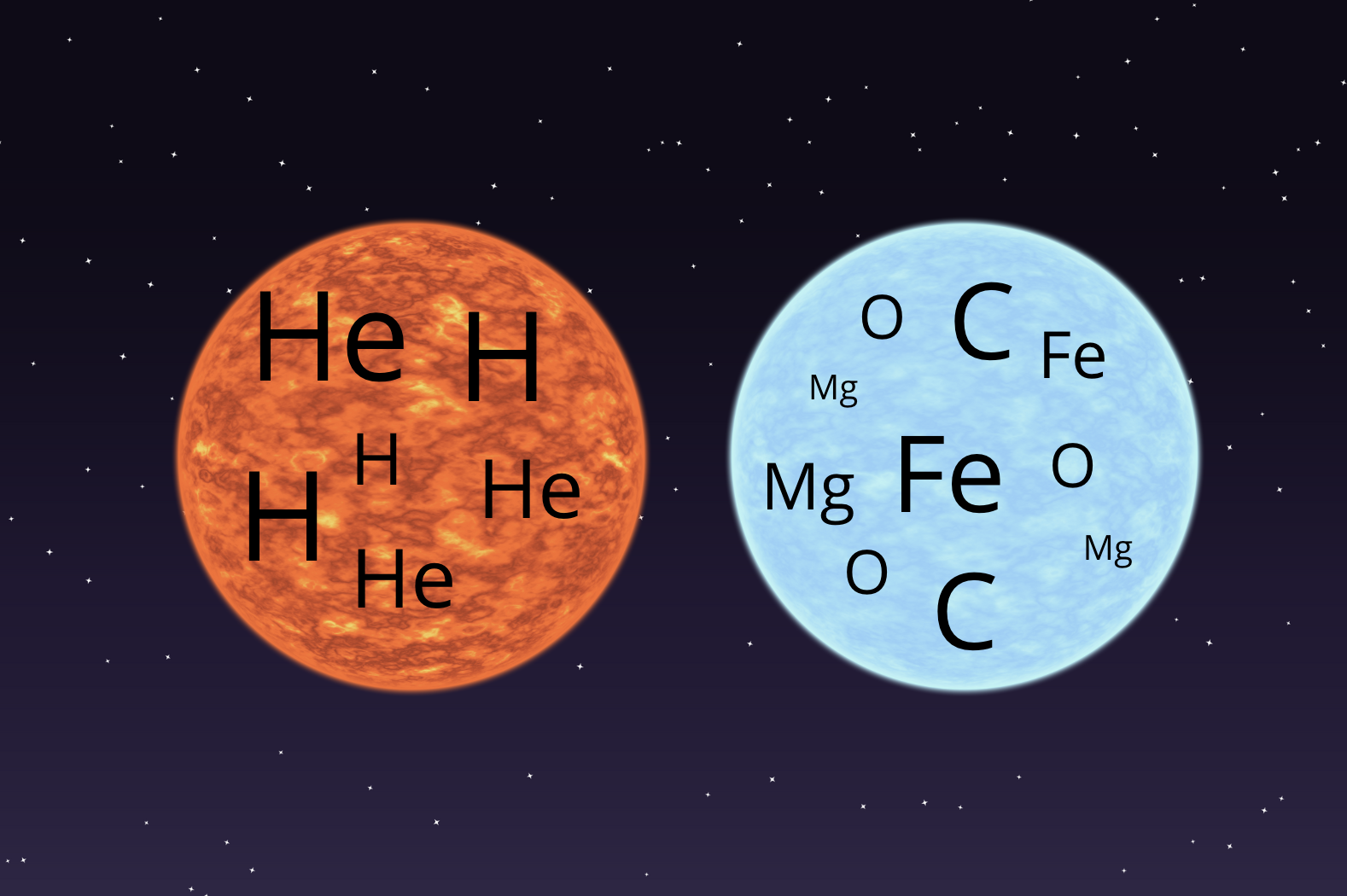
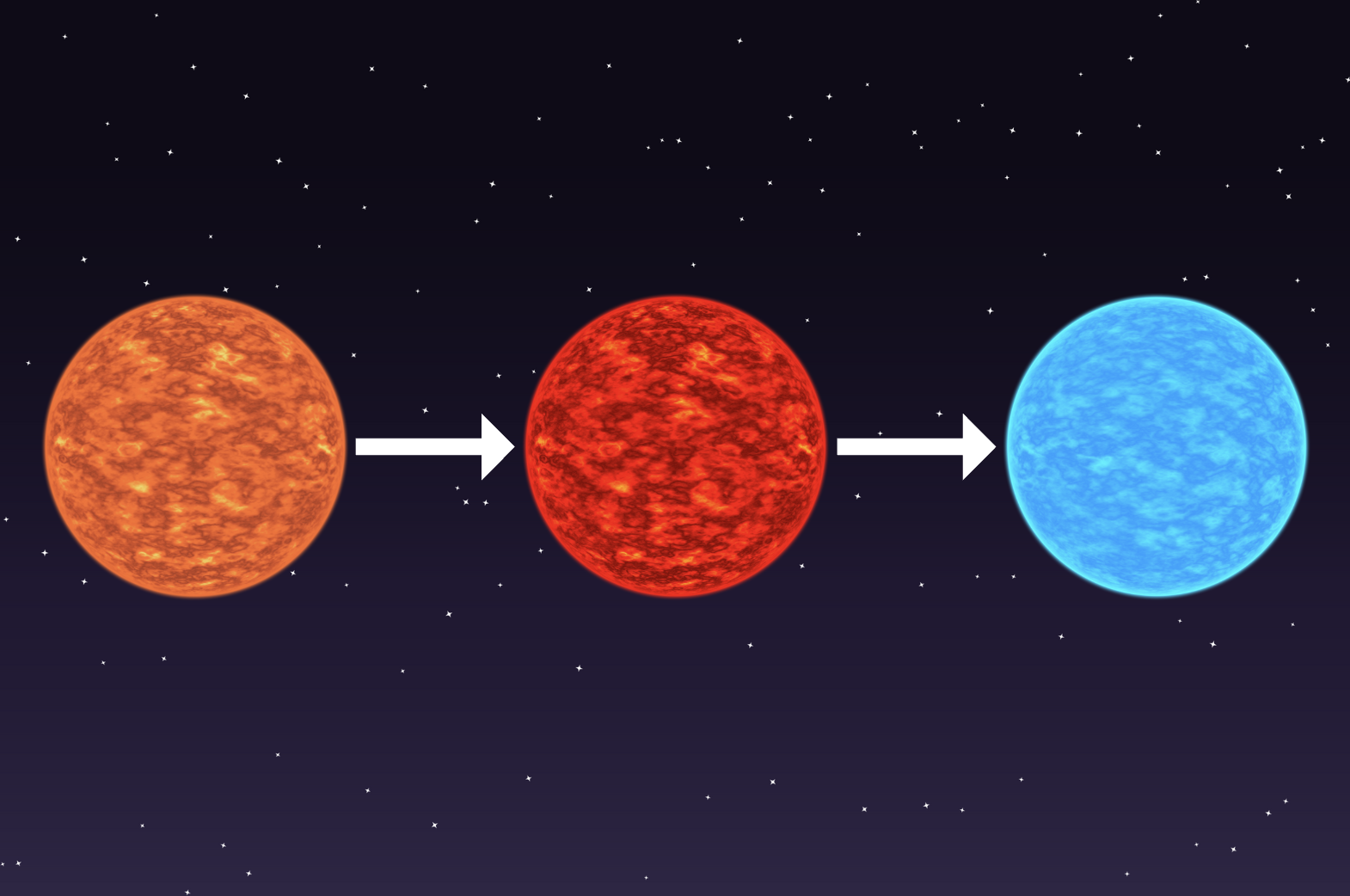
"From our perspective on Earth, stars seem to twinkle because their light passes through Earth's atmosphere, which is not perfectly still. As the light travels through the atmosphere, it bends in different directions, causing the star's brightness to change slightly."
The Digital Package is ideal for those short on time. Register a star’s name and receive all documents via email in under 15 minutes, ready to download and print at home!