Delphinus Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Delphinus (The dolphin)
Delphinus is a constellation located in the northern celestial hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from the Latin "Dolphin" and means Dolphin.
The location of the constellation Delphinus is essentially in the northern hemisphere, and we can find it in the night sky all year round. Still, the best season to see it is during the summer.
Delphinus is a small and very faint constellation, so it is not easy to see in the sky.
The brightest star in Delphinus is Rotanev (β Delphini / β Del / 6 Delphini) which has a magnitude de +4.2.
Although the constellation Delphinus is small, it is also home to deep-sky objects such as globular clusters and Nebulae.
In addition, within the constellation's boundaries, there are occurrences of a sporadic meteor shower.

The Mythology And History Of The Delphinus Constellation
Greek Mythology


Delphinus is related to a story from Greek mythology of the seventh century BC about the Greek poet Arion of Lesvos.
In the myth, Arion was back home on a ship because, during his life, he had amassed great wealth; this caused the crew to riot against him to take his money.
When he was about to die, Arion asked to be granted one last wish; this desire was to sing; while the crew was distracted by his song, Arion plunged into the sea to almost certain death.
He was rescued by a Dolphin who had been enchanted with his song.
So Arion would reach the coast of Laconia riding on the back of the dolphin. And in honor of his work, Poseidon placed the dolphin in the stars, immortalized in a constellation.
Early Modern Period


After being considered a constellation independent of the others in 1922, the astronomer Eugène Delporte drew the official boundaries of the most recent constellations; Delphinus was among those constellations.
A polygon of 14 segments defines the official boundaries of the constellation Delphinus. 5 stars form the main stars that shape the figure of the dolphin.
They are shaped like a quadrilateral with a star in one of the corners representing the dolphin's tail.
Nowadays


Since its annex as a constellation, Delphinus has not undergone significant changes in its borders. In the field of research, it is a region with substantial concentrations of stars that serve to study the evolution of the solar system.
How To Find The Delphinus Constellation?
Visibility By Region
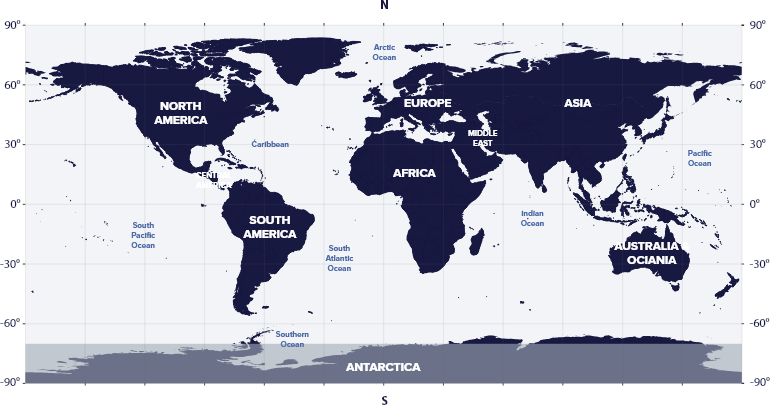

The constellation Delphinus resides in the fourth quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere (NQ4), at latitudes between 69° S and 90° N, which means we can see the constellation in the night sky in every country in the world, including a small section of Antarctica.
Delphinus is visible in the USA, Europe, Russia, Asia, China, and Japan in the northern hemisphere.
Delphinus is visible in all countries such as Brazil, Argentina, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica in the south.
Visibility By Season
Delphinus is a constellation near the north pole, so it is visible throughout the year to the northern hemisphere countries; the best time to see it is in September.
For the southern hemisphere countries, a section of the constellation is no longer seen in spring.
Finding Delphinus Constellation


To locate the constellation Delphinus, you must look to the north of the celestial vault.
Delphinus is a small constellation with very faint stars. You will probably have to use binoculars to find it if you live in an urban area or with light pollution.
In terms of navigation, the best way to find the constellation Delphinus is to draw an imaginary line from the star Altair of the constellation Aquila to the constellation Pegasus ion. Delphinus is located right in the middle of the two.
Related Constellations
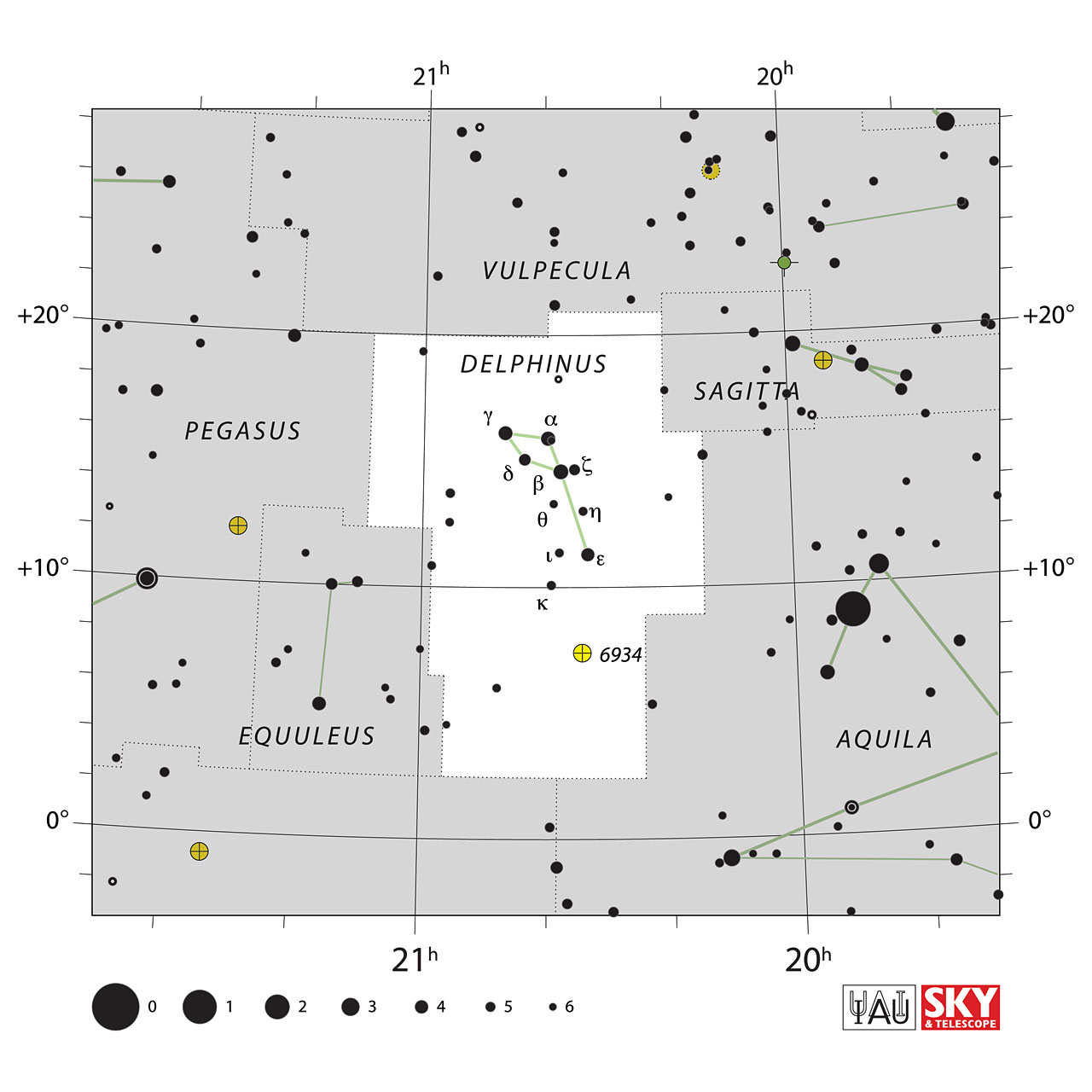

The bordering constellations of Delphinus are Vulpecula, Sagitta, Aquila, Aquarius, Equuleus, and Pegasus.
In addition, the constellation Delphinus belongs to the family of constellations of the Celestial Waters; these include the constellations Carina, Columba, Equuleus, Eridanus, Piscis Austrinus, Puppis, Pyxis, and Vela.
Stars in Delphinus Constellation
Officially the constellation Delphinus has 44 stars, of which 5 form the central figure of the dolphin; these are Rotanev, Sualocin, Gamma Delphini, Deneb Dulfim, and Delta Delphini.
Rotanev (β Delphini / del β / 6 Delphini)
It is the brightest star in the constellation with magnitude 3.6; it is multiple stars of five components, although only two of them are physically related. It is located 97 light-years from our solar system.
Sualocin (α Delphini / del α / 9 Delphini)
Although its assignment letter is A, it is not the brightest de Delphinus since it has a magnitude of 3.8; it is the second brightest star in the constellation.
It consists of seven-component multiple stars, of which only two of them are gravitationally coupled.
ε Delphini (Aldulfin or Deneb Dulfim)
Located 360 light-years away, ε Delphini is a bluish-white star of magnitude 3.95, the third brightest in the constellation Delphinus.
Other Delphinus Stars:
- γ Delphini is a binary star composed of an orange subgiant and a yellow dwarf.
- δ Delphini: Variable star of magnitude 4.43. It is part of the asterism called the Coffin of Job.
- ζ Delphini: A white main-sequence star of magnitude 4.68.
- η Delphini: White subgiant of magnitude 5.39.
- θ Delphini: Orange supergiant of magnitude 5.70.
- ι Delphini: White star of magnitude 5.42.
- κ Delphini: Yellow subgiant of magnitude 5.07.
- ρ Aquilae: Although this star belongs to the constellation of Delphinus, its name refers to the constellation Aquila. Its magnitude is 4.94.
- 13 Delphini: A white main-sequence star of magnitude 5.61.
- 15 Delphini: Double star of magnitude 6.01.
- 16 Delphini: A white star of magnitude 5.54.
- 18 Delphini: Yellow giant with an exoplanet.
- R Delphini: Variable type Mira of variable brightness.
- U Delphini: Red giant and semi-irregular variable.
- W Delphini: Eclipsing binary of magnitude 9.69.
- TY Delphini: Eclipsing binary of magnitude 9.7,
- EU Delphini: Red giant and semi-irregular variable.
- LS Delphini: Binary of magnitude 8.65.
- MR Delphini: Triple star system.
- NGC 6891: Planetary Nebula
- HD 194598: Star from the galactic halo.
- HD 195019: A binary star with an exoplanet of the "hot Jupiter" type.
- HD 196885 (HR 7907): Yellow subgiant with an extrasolar planet.
- WASP-2: Orange dwarf with an exoplanet of the "hot Jupiter" type.
Deep Sky Objects


Delphinus is also home to deep sky objects. Deep-sky objects are celestial bodies different from stars, such as nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies) or galaxies.
In the case of Delphinus, it only has four identifiable deep-sky bodies, these are:
- NGC 6891: Bluish planetary nebula is located 7200 light-years from Earth.
- NGC 6905: Planetary nebula with a central star of magnitude 12.5.
- NGC 6934: Globular cluster of magnitude 9.75.
- NGC 7006: Globular cluster of magnitude 12.0 located 135,000 light-years away.
Meteor Showers


The constellation Delphinus has associated a very faint meteor shower that has been seen only a couple of times since 1930; this shower of stars is called "Gamma Delphinids."
Calculations by NASA indicate that the shower of Gamma Delphinids occurs between June 10 to 11 and has its peak of observation since June 11.
Conclusions
- Delphinus is a constellation of the northern celestial hemisphere; its name comes from the Latin "Dolphin" and means Dolphin.
- Although it is in the Northern Hemisphere, Delphinus see all world countries, including a small section of Antarctica.
- The best month to see the constellation Delphinus is in September.
- The brightest star in Delphinus is Rotanev (β Delphini / β Del / 6 Delphini) which has a magnitude of +4.2.
- The best way to find the constellation Delphinus is to draw an imaginary line from the star Altair of the constellation Aquila to the constellation Pegasus. Delphinus is between the two.
- The most popular Delphinus meteor shower is called gamma Delphinids.







