Carina Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Carina (The keel)
Carina is one of the brightest and most prominent constellations in the southern celestial hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from Ancient English and means "The Helmet," the lowest part of a ship.
Carina occupies an area of 494 square degrees, which places it in the 34th place of the most prominent constellations.
The location of the constellation Carina is essentially in the southern hemisphere, so it is impossible to visualize it in most countries of the northern hemisphere.
The brightest star in the constellation Carina is Alpha Carinae (α Car), better known as Canopus, which has an apparent magnitude of -0.72, being the second brightest star in the entire night sky.
The constellation Carina is home to deep-cool objects such as nebulae and star clusters.
In addition, within the boundaries of the constellation Carina, there are occurrences of an essential meteor shower.

The Mythology And History Of The Carina Constellation
Ancient Egypt


In the ancient Egyptian culture, there was a constellation called Argo Navis, which occupied the regions currently occupied by the constellations of Carina, Vela, and Puppis; this constellation was associated with the "Ship of Osiris," an essential Egyptian god.
Greek Mythology


In ancient Greece, Carina was still part of the constellation Argo Navis; however, in this culture, this constellation was associated with Jason's large ship and the Argonauts who were looking for the Golden Fleece.
Early Modern Period


In 1763 astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille divided the constellation Argo Navis into three sections because it was too large to be a single constellation; it was 28% larger than Hydra, the most prominent constellation today.
Being so large, it had too many stars of great luminosity that required a separate designation, so it was divided into three constellations Carina, Vela, and Puppis.
Nowadays


In the twentieth century, the International Astronomical Union added the constellations Carina, Vela, and Puppis to 88 official constellations and considered them independent.
There are still celestial maps where that region of the sky is still represented with the constellation Argo Navis, but officially it is no longer considered for academic writings.
How To Find The Carina Constellation?
Visibility By Region
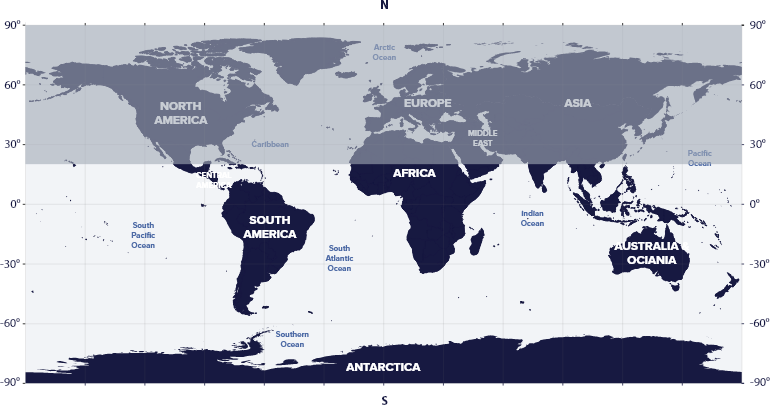

Carina resides in the second quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (SQ2) at latitudes between 20° N and 90° S, which means that we can see the constellation in the night sky from all countries of the southern hemisphere of the earth and some countries of the northern hemisphere.
The constellation Carina is visible in America, Asia, Australia, and Antarctica.
Carina is not visible in areas above 20° N latitude, such as the USA, Europe, Egypt, Japan, Canada, and Russia.
Visibility By Season
Carina is a constellation that can be seen most of the year in the southern hemisphere; however, March is the best month to visualize it.
The constellation Carina is visible only in late winter and early spring in the northern hemisphere.
Finding Carina Constellation
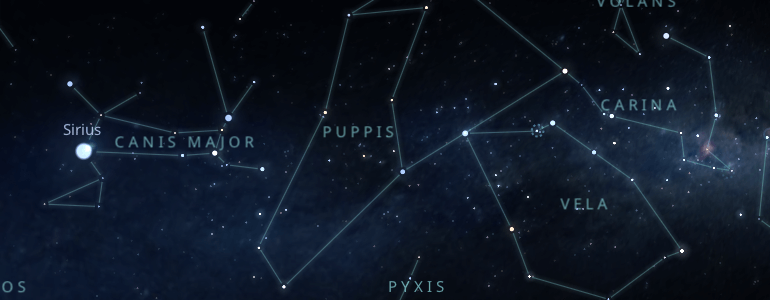

Carina is essentially close to the celestial equator, so if you are in the northern hemisphere, you will have to turn your gaze to the south. You can help yourself find Carina by looking for Canopus, the second brightest star in the sky.
One way to locate the constellation Carina is by finding its brightest star Canopus, at the end of the constellation closest to the south pole.
The easiest way to locate the constellation Carina is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the star Sirius towards the north pole. The star Canopus is located right in the middle of the road; once you locate Canopus, you will be able to visualize the rest of the constellation.
Related Constellations
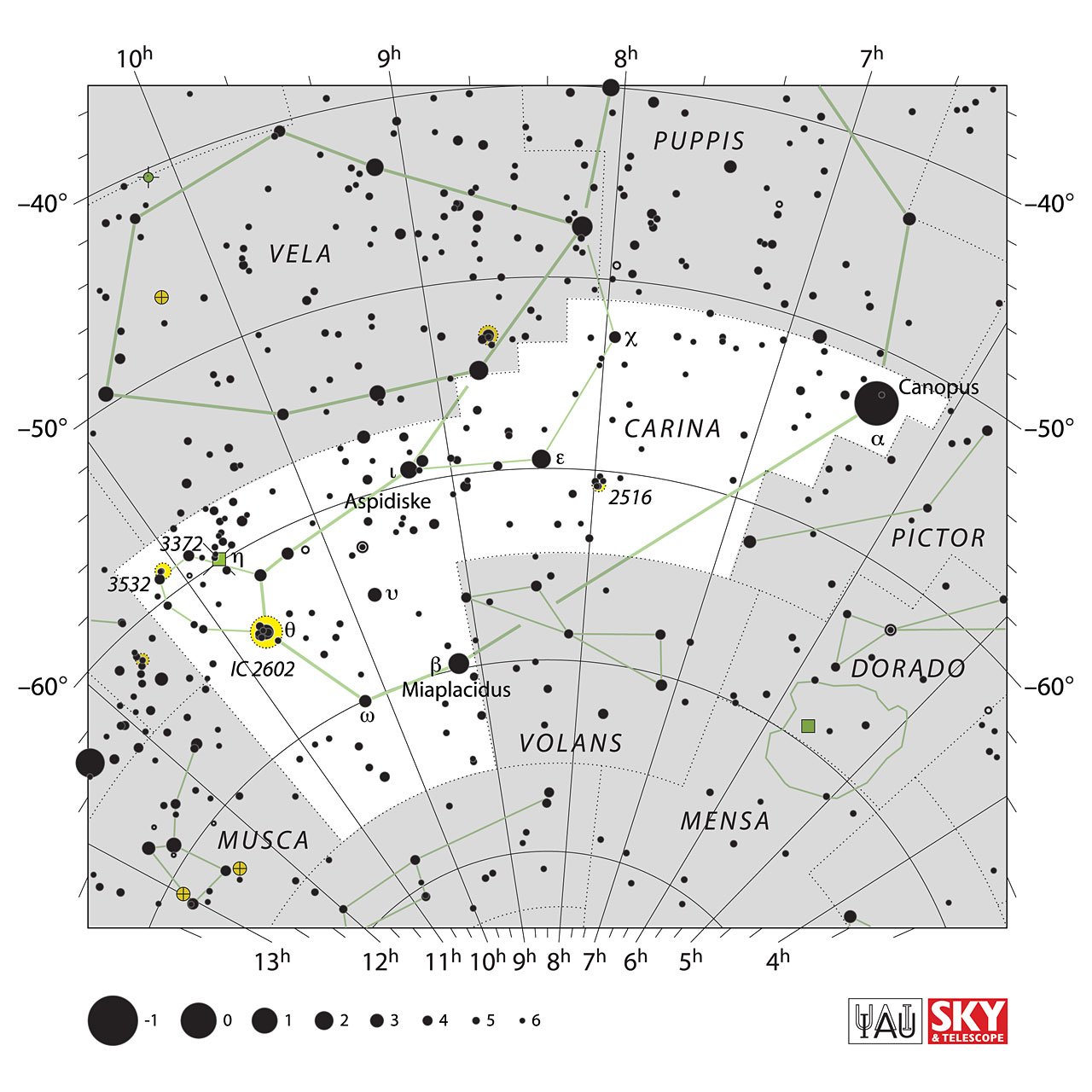

Stars in Carina Constellation
The constellation Carina officially contains 225 stars, of which 9 form the central figure of the constellation; these are Canopo, Miaplacidus, Avior, Aspidiske, Theta Carinae, Upsilon Carinae, Omega Carinae, Foramen, and Chi Carinae.
Canopus (α Cariane / Alfa Carinae )
With an apparent magnitude of -0.72, Canopus is the brightest star in the constellation Carina and the second brightest in the night sky behind only the star Sirius.
Canopus is a luminous giant or white-yellow supergiant of spectral type F0II with a surface temperature of 7280 K, located 309 light-years from earth.
Miaplacidus (Miaplácidus / Beta Carinae / β Car / HD 80007)
Located at a distance of 111 light-years from the solar system Miaplacidus is the second brightest star in the constellation Carina with an apparent magnitude of +1.67.
Miaplacidus is a white subgiant of spectral type A2IV with an effective temperature of 9100 K. Its luminosity is 210 times higher than the sun's luminosity, and its radius is almost six times larger than that of the Sun.
Other Carina Stars:
- ε Carinae (Avior)
- η Carinae (Eta Carinae)
- ι Carinae (Aspidiske)
- υ Carinae
- χ Carinae (Drys)
- h Carinae (HD 83183)
- I Carinae (HD 90589)
- b2 Carinae (HD 77370)
- f Carinae (V334 Carinae)
- S Carinae
- RT Carinae
- VY Carinae
- AG Carinae and HR Carinae:
- EM Carinae
- CK Carinae and IX Carinae
- PP Carinae (p Carinae)
- QX Carinae
- V337 Carinae (q Carinae)
- V382 Carinae
- V415 Carinae (A Carinae)
- BO Carinae
- V528 Carinae
- LHS 288
- GJ 1128
- HD 93129
- HD 93250
- A1 (WR 43a)
- WR 20a
- WR 22
- WD 0800-533
Deep Sky Objects


Carina is also known as home to several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies), or galaxies.
In the case of Carina, it is rich in galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters, being one of the constellations with the most incredible diversity of deep-sky bodies.
Keel Nebula / Carina Nebula / Eta Carinae Nebula or NGC 3372
The Keel Nebula is one of the largest in the sky, being about four times larger and brighter than the famous Orion Nebula.
This nebula contains several stellar nebulae inside, as well as a large number of stellar cumulus that give it an excellent brightness, which makes it the brightest nebula with the naked eye.
Other Deep-sky Objects In Carina:
- NGC 2516: Occasionally called the Southern Manger for its similarity to M44, it is a large open cluster found 1300 light-years away.
- NGC 2808: It is a large globular cluster, one of the most massive in our galaxy. It has stars from three different generations.
- NGC 3114: Open cluster.
- NGC 3293: Open cluster with more than one hundred stars 9000 light-years away.
- NGC 3532: It is an open cluster with about 150 stars.
- NGC 3603: It's a distant open cluster with several massive and hot Wolf-Rayet stars such as the A1 system.
- Theta Carinae or South Pleiades (IC 2602): It is a stellar cumulus containing about 74 stars, the most prominent being θ Carinae. It is the third brightest cluster in the sky and is located about 550 light-years away.
- NGC 2867: Planetary nebula whose central star is a Wolf-Rayet star.
- MSH 11-61A and MSH 11-62: Both are supernova remnants.
- Carina dwarf: Small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way.
Meteor Showers


In the region that comprises the constellation of Carina, a meteor shower called Eta Carinids occurs, which runs from January 14 to 27 of each year, reaching its peak of maximum observation on January 21.
Conclusions
- Carina is a constellation located primarily in the southern hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from Latin and means keel, which is the bottom part of the ship."
- Carina was initially part of the constellation Argo Navis, but because it was huge, it was divided into three parts: the constellation Carina.
- The best month to see the Carina constellation is in March, between the latitudes of 20° N and 90° S.
- The easiest way to locate the constellation Carina is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the star Sirius towards the north pole. The star Canopus is located right in the middle of the road; you can see the rest of the constellation.
- The brightest star in the constellation Carina is Alpha Carinae (α Car), better known as Canopus, which has an apparent magnitude of -0.72.
- The most notable deep sky body in the constellation Carina is the nebula NGC 3372.
- The most crucial shower of stars in the constellation Carina is the "Eta Carinids."







