Centaurus Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Centaurus (The Centaur)
Centaurus is one of the largest and most prominent constellations in the southern celestial hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from the ancient Greek culture of Centaurus.
The Centaur was a mythological creature half human and half horse, not to be confused this constellation with the constellation Sagittarius of the northern hemisphere.
The location of the constellation Centaurus is essentially in the southern hemisphere. Still, it is possible to visualize it in some northern hemisphere countries. We can find it in the night sky throughout the spring.
The constellation Centaurus is one of the largest and is easy to see. The brightest star in the constellation is Alpha Centauri (α Centauri / Rigil Kentaurus) which has an apparent magnitude of -0.01, being the fourth brightest in the sky.
The constellation Centaurus is home to deep-sky objects such as galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters.
In addition, within the boundaries of the constellation Centaurus, there are occurrences of an essential meteor shower.

The Mythology And History Of The Centaurus Constellation
Ancient China


In ancient China, the brightest stars of the constellation Centaurus, including α Centauri, θ Centauri (or Menkent), ε Centauri, and η Centauri, can be seen in the sky. Still, it is impossible to see all the stars belonging to Centaurus since China is located too far north.
Chinese astronomer Xu Guangqi managed to classify invisible stars among southern asterisms based on his star charts.
In Chinese astronomy, he added the stars of Centaurus are found in three different areas: the Blue Dragon of the East (Dōng Fāng Qīng Lóng in Chinese), the Vermilion Bird of the South (Nán Fāng Zhū Què in Chinese), and the Asterisms of the South. (Jìnnánjíxīngōu in Chinese).
Greek Mythology


Zeus decided to kill Ixion, king of Thessaly, to live among the gods in Greek mythology. However, Ixion tried to seduce Hera, with whom he slept. From there, Kentauros was born, a creature with the legs and body of a horse and the head, arms, and torso. Later this name was translated as Centaurus.
Kentauros fathered with mares the Centaurs, a new race of creatures equal to him. This race did not respect the laws of hospitality, nor did they follow the rules of peaceful coexistence; all were violent except for Chiron.
Chiron was a centaur who mentored several heroes, such as Hercules, Achilles, and Theseus. In one of his many battles, Chiron died from a poisoned arrow, and in honor of his actions, Zeus placed him among the constellations of the sky.
Early Modern Period


At the beginning of the fifth century, the constellation Centaurus was even more significant than it is today because the constellation of Lupus was considered an asterism within the constellation Centaurus.
In turn, the constellation "Southern Cross" is also considered an asterism within the limits of Centaurus. Lupus and the Southern Cross were reassigned as independent constellations of Centaurus later.
Centaurus acquired the limits it currently has during the tenth century. Since then, it has not undergone significant changes in its limits.
Nowadays


Since the constellation Lupus and the Southern Cross were removed, Centaurus has not changed its boundaries. It remains one of the most prominent constellations in the southern sky.
It occupies an area of 1,060 square degrees, making it the ninth most prominent constellation in the night sky.
How To Find The Centaurus Constellation?
Visibility By Region
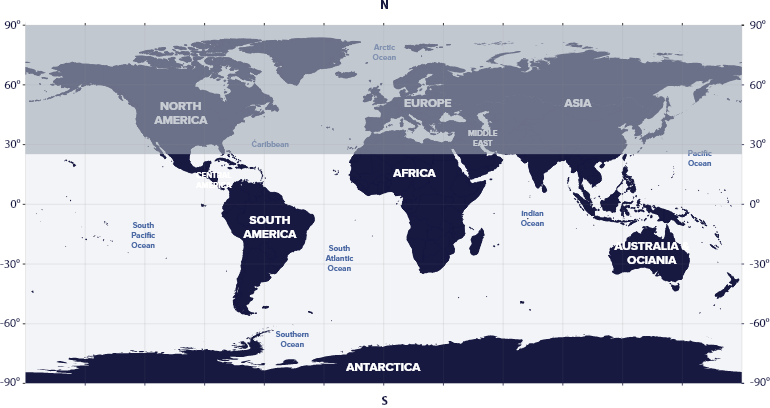

Centaurus resides in the third quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (SQ3) at latitudes between 25° N and 90° S, which means that we can see the constellation in the night sky from all the countries of the southern hemisphere of the earth and some countries of the northern hemisphere.
Centaurus is visible in South America, Asia, Australia, and Antarctica.
Centaurus is not visible in areas above 25° N latitude, such as the USA, Europe, Russia, China, Japan, northern Mexico, or Egypt.
Visibility By Season
Centaurus is a circumpolar constellation most visible during the spring; however, May is the best month to visualize it.
In the northern hemisphere, the constellation Centaurus is visible during some autumn days, but only if there are clear skies and high areas because it is very close to the horizon.
Finding Centaurus Constellation
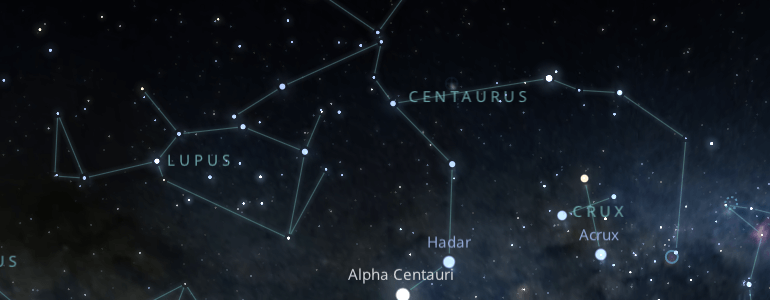

One way to locate the Centaurus constellation is by finding its brightest star Alpha Centauri, which is in the southernmost part of the constellation and one of the brightest stars in the southern hemisphere.
The easiest way to locate Centaurus is with the help of the constellation Crux.
As its name indicates, this constellation is shaped like a cross and is located just below Centaurus.
The easiest way to locate the constellation Centaurus is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the constellation Crux to the constellation Lupus; in the middle of both, you will find the brightest stars of Centaurus Alpha Centauri and Hadar.
Related Constellations
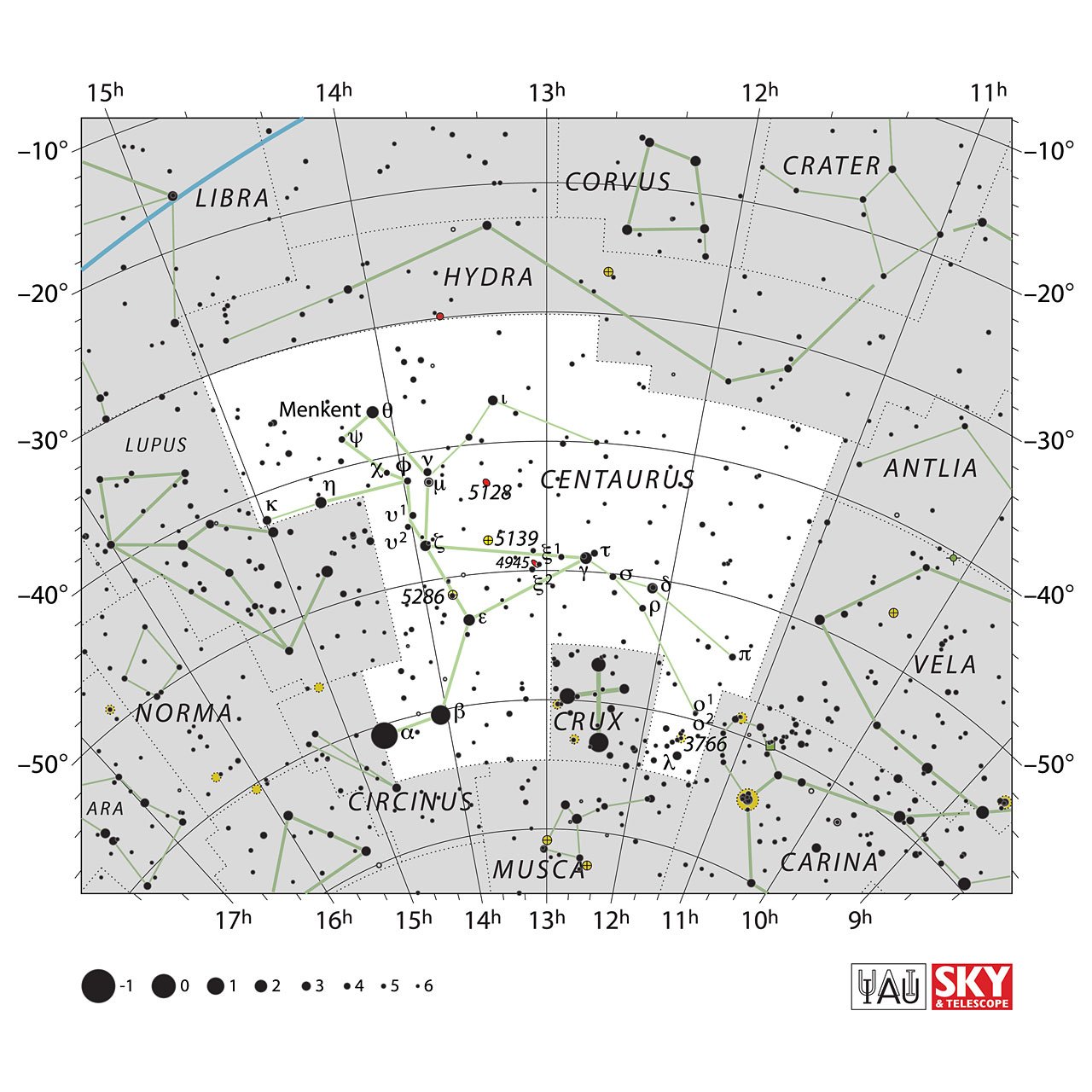

Centaurus's constellations are Antlia, Carina, Circinus, Crux, Hydra, Libra (corner), Lupus, Musca, and Vela.
Historically Centaurus belongs to the Hercules family of constellations; Aquila, Ara, Corona Australis, Corvus, Crater, Crux, Cygnus, Hercules, Hydra, Lupus, Lyra, Ophiuchus, Sagitta, Scutum, Serpens, Sextans, and Triangulum.
Stars in Centaurus Constellation
The constellation Centaurus officially contains 281 stars, of which 14 form the main figure of the centaur, these are Rigel Kentaurus, Hadar, Menkent, Muhlifain, Epsilon Centauri, Eta Centauri, Alnair, Ma Wei, Alhakim, Ke Kwan, Nu Centauri, Mu Centauri, Pi Centauri and Sigma Centauri.
ALPHA CENTAURI
The Alpha Centauri system is located 4.5 light-years away. It is the brightest star in the constellation Centaurus with an apparent magnitude of +0.01.
It is the closest star system to ours; it has three main stars, Alpha Centauri A (Better known as Rigel Kentaurus), Alpha Centauri B (better known as Toliman), and Alpha Centauri C (better known as Proxima Centauri)
The three stars make up the star system. It is known that in Proxima B, there is an exoplanet that could have the conditions to have liquid water and possibly life.
Hadar or Agena (Beta Centauri / β Cen)
Agena is the second brightest star in the constellation Centaurus with an apparent magnitude of +0.60.
It is a blue-white giant star that lies between 350 and 390 light-years away.
Menkent (θ Centauri / θ Cen / 5 Centauri)
Menkent is an orange giant star located 61 light-years from the solar system, with a magnitude of +2.06 is the third brightest star in the constellation Centaurus.
Other Centaurus Stars:
- Centauri γ
- δ Centauri
- Centauri ε
- Centauri ζ
- Centauri η
- ι Centauri
- τ Centauri
- Centauri ψ
- C2 Centauri
- j Centauri (HD 102776)
- 1 Centauri
- 2 Centauri
- 3 Centauri
- R Centauri
- T Centauri
- U Centauri
- V Centauri
- RR Centauri
- SS Centauri
- SV Centauri
- SZ Centauri
- TT Centauri
- UY Centauri
- XX Centauri
- V761 Centauri
- κ Centauri
- λ Centauri
- Centauri μ
- ξ² Centauri
- ρ Centauri
- Centauri σ
- V824 Centauri (HD 114365)
- Krzeminski Star (V779 Centauri)
- (Centaurus X-3)
- HR 4523 (HD 102365)
- HR 4796 (HD 109573)
- HD 101930
- HD 114386
- HD 113538
- HD 113766
- HD 114729
- HD 116713
- HD 131399
- Gliese 438
- Gliese 542 (HD 125072)
- Gliese 435 (HD 101581)
- Przybylski Star (HD 101065)
- GJ 3770 (WD 1310-472).
Deep Sky Objects


Centaurus is also known as home to several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies), or galaxies.
In the case of Centaurus, it is rich in galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters, being one of the constellations with the most incredible diversity of deep-sky bodies.
Omega Centauri (NGC 5139)
It is the most amazing deep-sky body in the constellation Centaurus. Omega Centauri is visible without the need for telescopes.
It orbits the Milky Way and is one of the largest and brightest globular clusters associated with our galaxy. It contains several million Population II stars with 12 million years.
Other Deep-sky Objects In The Constellation Centaurus:
- NGC 3766: Also known as the Pearl Cluster, it is an open cluster discovered by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1752.
- NGC 3918: Planetary nebula of magnitude 8.1. It has an approximately spherical outer envelope located about 3000 light-years away.
- NGC 5307: The most distant planetary nebula—about 10,000 light-years—of magnitude 11.2. It has a very symmetrical windlass or spiral structure.
- IC 2944: It is an open cluster with an associated emission nebula.
- Boomerang Nebula: It is a planetary proto nebulous whose temperature of 1 K makes it the coldest known object in the universe.
- RCW 86: It is a remnant of supernova SN 185.
- SNR G292.0+01.8: It is a supernova remnant.
- Kesteven 17: Supernova Remnant.
- SNR G306.3-00.9: Supernova remnant.
- NGC 4603: A spiral galaxy 107 million light-years away from the Centaur cluster.
- NGC 4622: Unbarred spiral galaxy is seen from the front. It has a very prominent ring structure located 111 million light-years away.
- NGC 4650A: Polar annular galaxy of magnitude 13.9.
- NGC 4696: Elliptical galaxy and the brightest member of the Centaurus. It is located 116 million light-years from Earth.
- NGC 4945: It is one of the brightest galaxies in the Centaurus A/M83 group. It is located 11.7 million light-years away.
- Centaurus A (NGC 5128): A distant lenticular galaxy approximately 14 million light-years. It is one of the closest radio galaxies to Earth, so professional astronomers have extensively studied its active galactic core. It is, at magnitude 6.9, the fifth brightest galaxy in the sky. 35
- NGC 5253: Irregular galaxy discovered by John Frederick William Herschel on March 15, 1787. It is part of the M83 subgroup within the Centaurus A/M83 group.
- NGC 5408: An irregular galaxy 15.7 million light-years away.
Meteor Showers


At least eight meteor showers occur in the region comprising the constellation Centaurus. The most notable are the following.
- Alpha centaurids: This occurs between January 28 to February 21. and is the brightest of all, the peak of maximum exposure is February 7.
- Beta Centaurids: This occurs from February 2 to 25.
- Omicron Centaurids: Occurs from January 31 to February 19.
- Theta Centaurids: This occurs from February 12 to 16.
Interesting Facts
- Frequently the constellation Centaurus is confused with the constellation Sagittarius since both are represented with the same mythological creature, the centaur, a creature with horse legs and the torso of a human.
- Centaurus is the ninth most prominent constellation in the sky.
- The Alpha Centauri star system is the closest to Earth.
Conclusions
- Centaurus is a constellation located primarily in the southern hemisphere; its name comes from the mythological creature of the Greek culture "Centaurus," consisting of a half-horse, half-human being.
- Centaurus is one of the largest and most prominent constellations in the sky. It contains the Alpha Centauri star system, which is the closest to earth.
- Centaurus is a southern constellation, but it is possible to see it from some countries in the northern hemisphere, such as India or Mexico.
- The best month to see the Centaurus constellation is in May, between the latitudes of 25° N and 90° S.
- Centaurus is one of the easiest constellations to locate because it is just above the Southern Cross. This very bright constellation marks the south pole.
- The easiest way to locate the constellation Centaurus is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the constellation Southern Cross to the constellation Lupus; in the middle of both, you will find the brightest stars of Centaurus Alpha Centauri and Hadar.
- The brightest star in Centaurus is Alpha Centauri, with an apparent magnitude of +0.01.
- The most notable deep-sky body in the constellation Centaurus is Omega Centauri, a globular cumulus seen with the naked eye.
- The strongest meteor shower in Centaurus is the "Alpha centaurids."
Sources Of Information:
- https://www.constellation-guide.com/constellation-list/centaurus-constellation/
- http://www.seasky.org/constellations/constellation-centaurus.html
- https://star-name-registry.com/constellations/centaurus
- https://www.universeguide.com/constellation/centaurus
- https://in-the-sky.org/data/constellation.php?id=20






