Hercules Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Hercules
Hercules is one of the largest and most prominent constellations in the earth's northern hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from ancient Rome, while the Greeks called it Heracles as it was the name of an essential hero and son of Zeus.
The location of the constellation Hercules is essentially in the northern hemisphere, and we can find it in the night sky throughout the summer.
The constellation Hercules is not so easy to see in the night sky, as it does not have stars of the first magnitude. Its brightest Star, β Herculis (Kornephoros), with a magnitude of 2.78.
The Hercules constellation is home to deep-sky objects such as galaxies, nebulae, and loom clusters.
In addition, within the constellation's boundaries, there are occurrences of a meteor shower.

The Mythology And History Of The Hercules Constellation
Ancient Egypt


The ancient Egyptians gave this constellation the name "Heracles" because this was the name of a famous warrior who had achieved incredible feats.
In one of the myths of ancient Egypt, it is narrated that "Heracles" fervently desired to see the god "Jove," one day he appeared to him. He took a ram from which he tore off his head and skin, giving it to Heracles to cover himself with it.
That is why Heracles is depicted covered in a skin of a calf. Later other cultures adapted these stories but changed the name of Heracles to Hercules.
Greek Mythology


Heracles is known as "Hercules," son of Zeus and Alcmena in Greek mythology. Hercules was the most important hero of the greeks, known for his great deeds and superhuman strength.
Among his incredible feats, the best known are "The 12 Works of Hercules", which consisted of a series of missions imposed by the prophet Sibylph.
In one of the myths, Hercules returns to Escalia after completing the 12 works. To celebrate the victory, he sacrificed twelve oxen in honor of Zeus.
His third wife, Deyanira, dead of jealousy and wanting to regain Hercules' attention, poured the blood given to her by the centaur Neso on her robe. However, this blood was a potent poison that ended up killing Hercules.
Upon learning of this, Zeus immortalized him by turning him into the constellation of Hercules.
Early Modern Period


After Greek civilization, the Romans took the story of Heracles, changing the name to Hercules.
From the fifth century, this is the name with which the constellation would be officially known throughout the world, being named the "Constellation of Hercules" in various official writings, including the 48 constellations Ptolemy.
Later during the fifteenth century, the constellation was delimited, reducing the area it occupied of the sky but still retaining its position as one of the largest and most important constellations in the northern hemisphere.
Nowadays


Since the fifteenth century, the constellation has not undergone significant changes. Its limits and number of stars have not changed.
The constellation Hercules does not have very bright stars. However, it is still an actual constellation because it is located in the northern hemisphere and serves as a guide to finding the north pole.
Many astronomers conduct essential research within the constellation regions because it has many star clusters and galaxies in the mountains.
How To Find The Hercules Constellation?
Visibility By Region
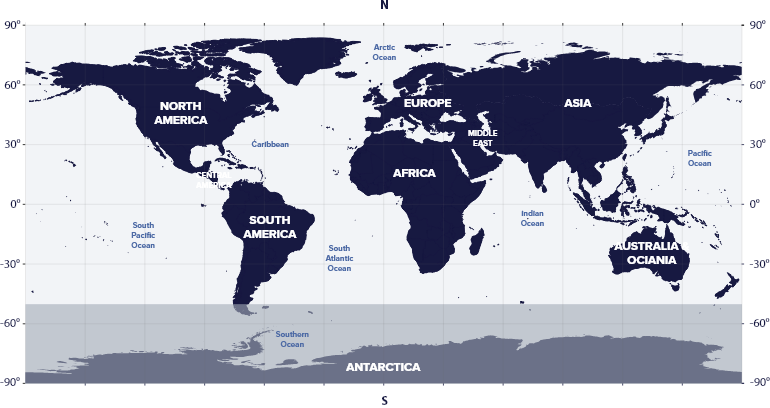

The constellation Hercules resides in the fourth quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere (NQ4), at latitudes between 50° S and 90° N, which means we can see the constellation in the nocturn sky in all countries of the northern hemisphere.
Hercules is visible from the southernmost regions of the planet, such as New Zealand, southern Chile, or the desired port in Argentina.
Hercules is visible in North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, except Antarctica.
Visibility By Season
Hercules is visible from late May to early August in both hemispheres, classified as a summer constellation in the northern hemisphere and winter in the southern hemisphere.
The best month to see the constellation Hercules is in July.
Finding Hercules Constellation


Hercules is the fifth most prominent constellation in the sky, but it isn't easy to find since it has bright stars.
The easiest way to locate Hercules in the sky is by using the stars near the constellation.
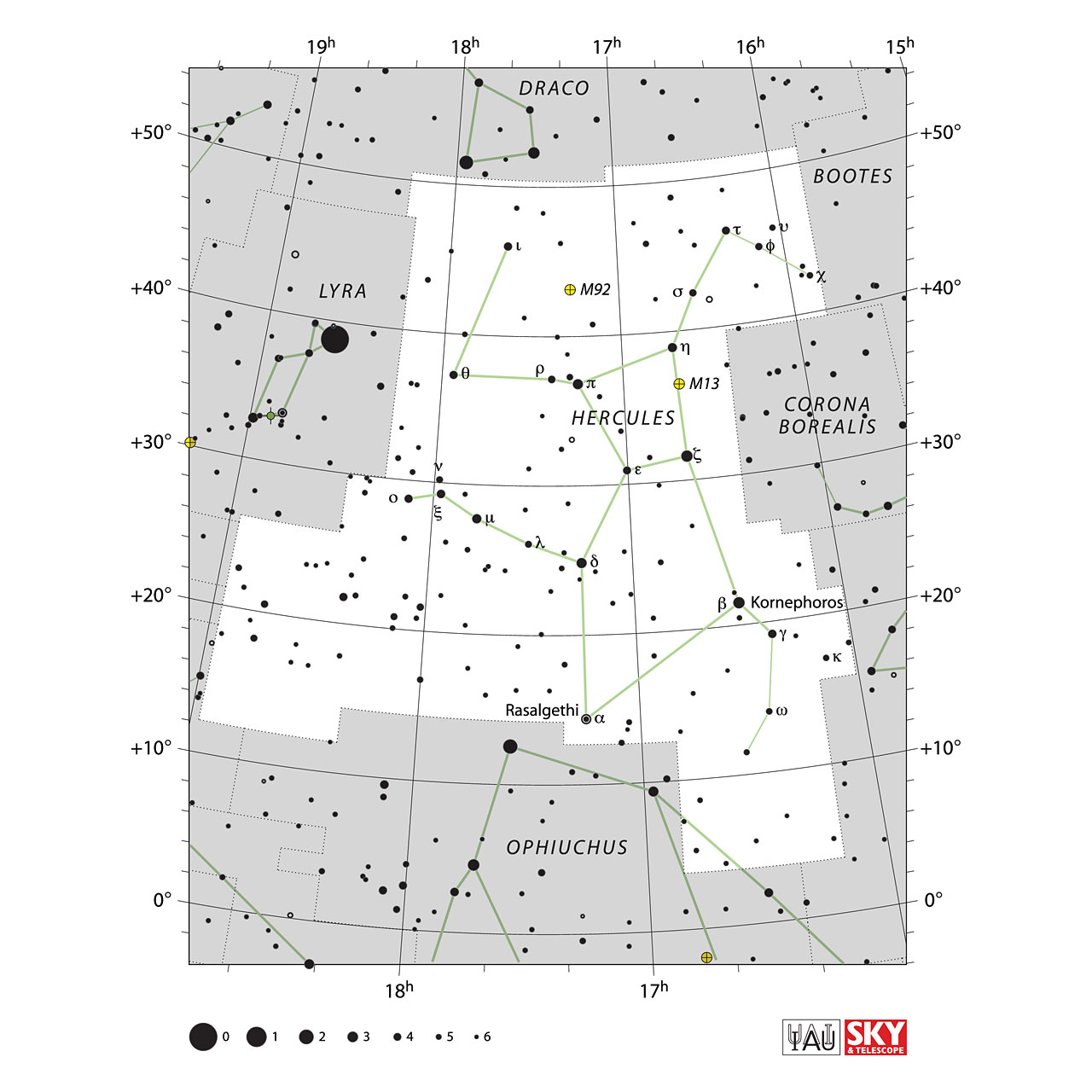
You can draw a straight line from the vega star of the constellation Lyra to the Star Arcturus of the constellation Bootes, in the middle of both constellations in the constellation of Hercules.
The main asterism of Hercules consists of 4 stars: Pi Herculis, Zeta Herculis, Epsilon Herculis and Eta Herculis.
Related Constellations

Stars in Hercules Constellation
Hercules is one of the most prominent constellations occupying an area of 1225 square degrees in the sky; because of this, it has a great diversity of stars.
Hercules' brightest Star is β Herculis, also called Kornephoros, which is 148 light-years away and has an apparent magnitude of 2.78.
ζ Herculis (Zeta Herculis)is the second most luminous star in the constellation with a magnitude of 2.89.
Subsequently, δ Herculis (Sarin) is next in brightness within the limits of the constellation and is a binary star system with a magnitude of 3.34.
Other Hercules Stars:
- α Herculis (Ras Algethi or Rasalgethi)is a quintuple star system.
- γ Herculis, White giant.
- ε Herculis, Spectroscopic binary.
- η Herculis, Yellow giant.
- θ Herculis, Orange luminous giant.
- ι Herculis, Blue Subgiant.
- κ Herculis A
- κ Herculis B
- λ Herculis (Maasym), orange giant.
- μ Herculis, yellow subgiant accompanied by two red dwarfs.
- π Herculis, Orange giant.
- Herculis φ
- ρ Herculis, Binary Star.
- σ Herculis, Binary star.
- φ Herculis, Spectroscopic binary.
- χ Herculis, Yellow dwarf.
- ω Herculis (Cujam or Kajam)
- 8 Herculis
- 14 Herculis, Orange dwarf.
- 30 Herculis (g Herculis), Redgiant.
- 53 Herculis
- 50 Herculis
- 68 Herculis, Eclipsing binary.
- 72 Herculis (w Herculis), Sun-like star.
- 89 Herculis, Yellow supergiant.
- 95 Herculis, Binary star.
- 99 Herculis, Binary Star.
- 101 Herculis, White giant.
- 109 Herculis, Orange giant.
- 110 Herculis, White-yellow star.
- 111 Herculis, White star.
- X Herculis, Variable star.
- SZ Herculis, Eclipsing binary.
- FN Herculis, Eclipsing Binary.
- UX Herculis, Eclipsing Binary.
- OP Herculis, Variable red luminous giant.
- HD 147506, Is a yellow subgiant with a massive planet.
- HD 149026, Is a Yellow Dwarf with a planet similar to Saturn's.
- HD 154345, Yellow Dwarf with a planet.
- Gliese 623, Binary Star
- Gliese 686, Red Dwarf.
- Gliese 649, Red Dwarf.
- HD 155358, Is a Star with two planets.
- Gliese 638, Orange Dwarf.
- HR 6806, Orange Dwarf.
- GD 362, Dwarf white.
Deep Sky Objects
Hercules is also home to several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects are celestial bodies different from stars, such as nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies) or galaxies.
M13 (NGC 6205 or Great Hercules Cluster)
It is between 22,200 and 25,000 light-years from Earth and is 145 light-years across.
M13 It is the most amazing deep-sky body in Hercules, is made up of several hundred thousand stars, the brightest of which is a red giant.
M92 (Messier 92 o NGC 6341)
It is found at a distance of about 26,000 light-years from Earth.
With an apparent magnitude of 6.3, M92 is one of the brightest globular clusters in the Northern Hemisphere.
The deep sky objects of Hercules are:
- NGC 6166, elliptical galaxy.
- NGC 6181, spiral galaxy.
- NGC 6207, spiral galaxy.
- NGC 6482, Is a very bright elliptical galaxy.
- 3C 348, giant elliptical galaxy.
- NGC 6210, reddish planetary nebula.
- Abell 39, spherical planetary nebula.
Meteor Showers


In the region comprising the constellation of Hercules occurs a meteor shower Tau Herculids.
This meteor shower takes place from May 19 to June 19, reaching its peak on June 9.
The body that originates this meteor shower is 73P / Schwassmann-Wachmann, which has an apparent magnitude of 11.5.
Interesting Facts
- Its original name is "Heracles,” also known as the constellation Hercules."
- The constellation of Hercules is usually depicted with the image of the warrior in a ram's skin robe. However, he is sometimes also represented with the skin of a lion.
- The official name is Hercules and not Heracles due to the Romans' influence on contemporary astronomy.
Conclusions
Hercules represents "The Warrior," which appears in the stories of different cultures from the Egyptians to the Romans.
In Greek mythology, he is poisoned by his wife by accident. In honor of his exploits, Zeus immortalizes him as a constellation.
Hercules is a constellation mainly located in the Northern Hemisphere. Still, it can be observed from all countries globally, except Antarctica, and the best month to see it is in July.
The constellation Hercules is the fifth largest in length, but it has very faint stars, so it is not so easy to see in the sky.
The best way to locate the constellation is through its neighboring constellations, Lyra and Bootes; by joining them with an imaginary line, we find Hercules.
Hercules' brightest Star is β Herculis, also called Kornephoros, which has an apparent magnitude of 2.78.
The most notable star cluster within the borders of Hercules is M13 (NGC 6205 or Great Hercules Cluster), which contains more than 8000 stars.
The strongest meteor shower in Hercules is Las Herculids.






