Eridanus Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Eridanus
Eridanus is one of the constellations located in the southern celestial hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from Greek history and means "Lesser River."
The location of the constellation Eridanus is essentially in the southern hemisphere, so it is not possible to visualize it in most countries of the northern hemisphere.
The constellation Eridanus is the sixth most prominent constellation in the night sky and is also the one that extends the most from north to south, covering an area of 1,138 square degrees.
The brightest star in the constellation Eridanus is Achernar (Alpha Eridani / α Eri / HR 472 / HIP 7588), with an apparent magnitude of +0.45.
In addition, within the boundaries of the constellation Eridanus, an essential meteor shower occurs.

The Mythology And History Of The Eridanus Constellation
Ancient Babylon


According to a theory based on the archaeological remains of Mesopotamia, the constellation Eridanus takes its name from the Babylonian constellation known as the Star of Eridu (MUL.NUN.KI).
Eridu was an ancient city at the southern tip of Babylon; located in the swampy regions, it was considered sacred to the god Enki-Ea, who ruled the cosmic domain of the Abyss, a mythical conception of the freshwater reservoir beneath the Earth's surface.
It is also thought that the Babylonians related the constellation to the Euphrates River.
Greek Mythology


Eridanus was mainly related to the myth of Phaethon, who took the flying chariot of Helios (the Sun) but did not have enough strength to control it and left it in different directions.
As Phaethon did not know how to direct the chariot of fire, sometimes the east comes very close to the earth, creating deserts and burning the skin of humans. Zeus intervened by knocking Phaethon down with lightning.
The constellation was initially considered to be the path traversed by Phaethon.
Nowadays


Currently, the constellation Eridanus remains the sixth most prominent constellation of the 88 existing, occupying an area of 1,138 square degrees in the night sky of the celestial southern hemisphere.
The constellation Eridanus is also a region of deep space bodies of paramount importance to modern science and astronomy in scientific research.
How To Find The Eridanus Constellation?
Visibility By Region
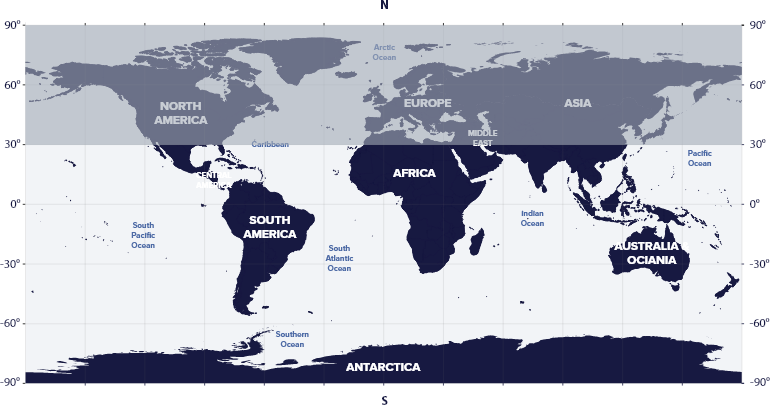

Eridanus resides in the first quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (SQ1) at latitudes between 32° N and 90° S. We can see the constellation in the night sky from all countries of the southern hemisphere of the earth and some countries of the northern hemisphere.
The constellation Eridanus is visible in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and Antarctica.
Eridanus is not visible in areas above 32° N latitude, such as Europe, the USA (except Florida), Canada, Japan, and Siberia.
Visibility By Season
Eridanus is a winter constellation, and December is the best month to visualize it.
In the northern hemisphere, the constellation Eridanus is visible only in winter.
Finding Eridanus Constellation
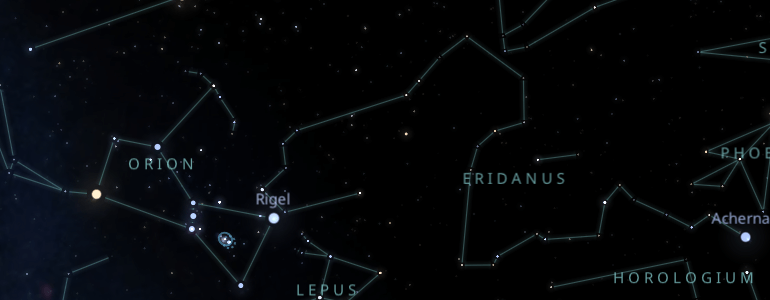

Eridanus is in the southern hemisphere, so you will have to direct your gaze to the south if you are in the northern hemisphere.
To find Eridanus, you can contact the star Rigel of the constellation Orion since both constellations are very close to each other.
The easiest way to locate the constellation Eridanus is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the constellation Phoenix to the constellation Reticulum.
In the middle of the road between the two, you will find the star Achernar, the brightest in the constellation Eridanus; from there, you can find the rest of the constellation.
Related Constellations
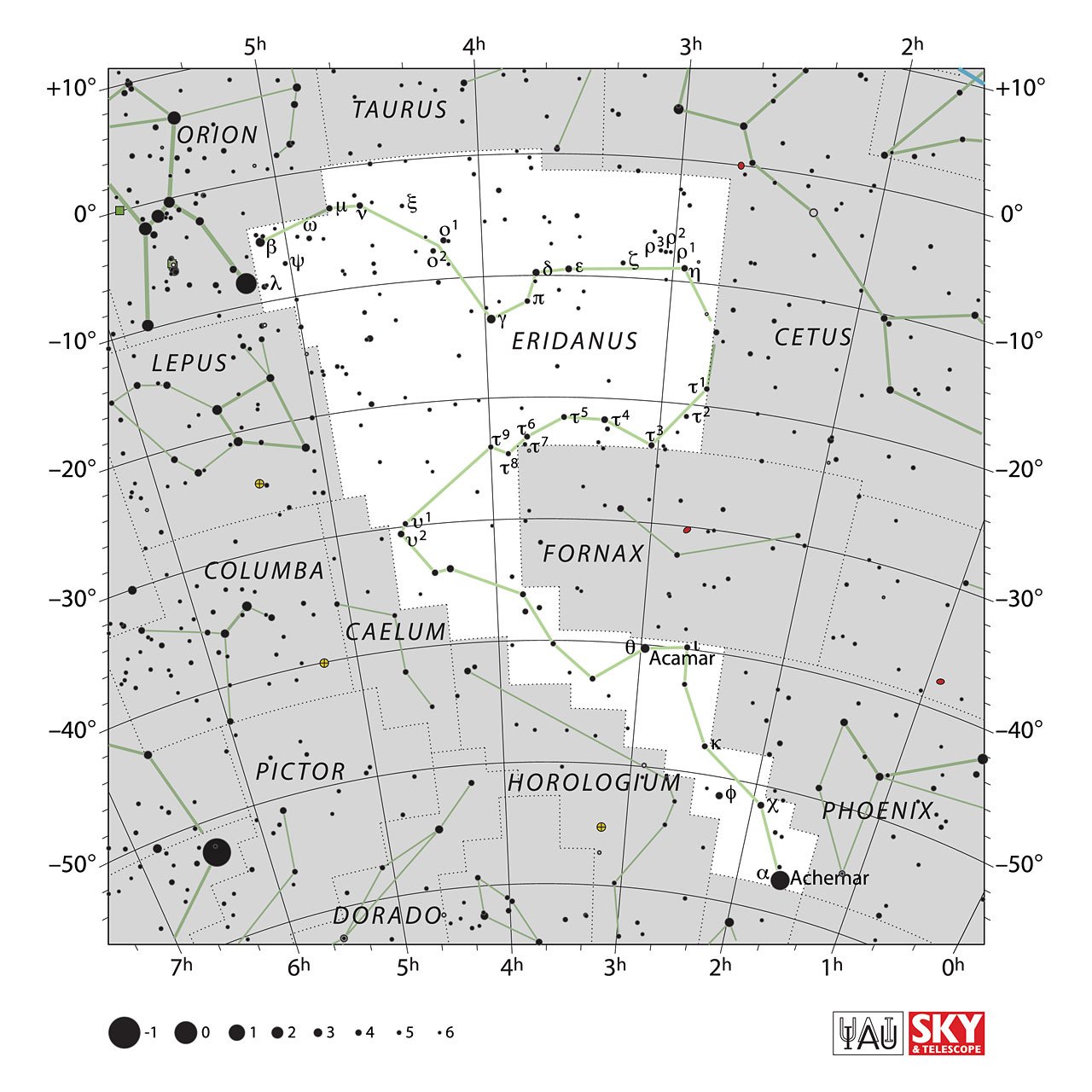

The constellations bordering Eridanus are Cetus, Fornax, Phoenix, Hydrus, Tucana (corner), Horologium, Caelum, Lepus, Orion, and Taurus.
In addition, Eridanus belongs to the Celestial Waters family of constellations, including Carina, Columba, Delphinus, Equuleus, Piscis Austrinus, Puppis, Pyxis, and Vela.
Stars in Eridanus Constellation
The constellation Eridanus officially contains 194 stars, of which 27 form the central figure of the constellation. These are:
Achernar, Cursa, Zaurak, Acamar, Rana, Tau-4 Eridani, Chi Eridani, Sadira, Theemim, Azha, Sceptrum, Nu Eridani, Mu Eridani, Beid, Tau-3 Eridani, Iota Eridani, Tau-6 Eridani, Kappa Eridani, Tau-5 Eridani, Pi Eridani, Keid, Tau-1 Eridani, Upsilon-1 Eridani, Tau-9 Eridani, Tau-8 Eridani, Angetenar and Zeta Eridani.
Achernar (Alpha Eridani / α Eri / HR 472 / HIP 7588)
It is the brightest star in the constellation Eridanus with an apparent magnitude of +0.45 and is located 144 light-years from the solar system.
Achernar is bluish-white with a very high rotation, so it has a flattened shape. It is also a variable of type Lambda Eridani.
Cursa (Beta Eridani / β Eri, 67 Eridani)
With an apparent magnitude of +2.78, Cursa is the second brightest star in the constellation Eridanus.
β Eridani is a star of spectral type A3 III. Luminosity class III indicates a giant star that has already consumed the hydrogen in the core.
Zaurak (γ Eridani / 34 Eridani)
Located 203 light-years from Earth, Zaurak is the third brightest star in the constellation Eridanus with an apparent magnitude of +2.98.
It is a red giant of spectral type M1IIIb whose superficial temperature is 3811 K, emitting a large amount of light in the infrared spectrum.
Other Eridanus Stars:
- Acamar
- Frog
- Tau-4 Eridani
- Chi Eridani
- Sadira
- Theemim
- Azha
- Sceptrum
- Nu Eridani
- Mu Eridani
- Beid
- Tau-3 Eridani
- Iota Eridani
- Tau-6 Eridani
- Kappa Eridani
- Tau-5 Eridani
- Pi Eridani
- Keid
- Tau-1 Eridani
- Upsilon-1 Eridani
- Tau-9 Eridani
- Tau-8 Eridani
- Angetenar
- Zeta Eridani
Deep Sky Objects


Eridanus is also known as home to several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies), or galaxies.
In the case of Eridanus, it is rich in galaxies and nebulae, being one of the constellations with the most incredible diversity of deep-sky bodies.
Galactic cumulus of Eridanus
Group of galaxies in the constellation Eridanus is made up of 200 galaxies. 73 have a size similar to or greater than the Milky Way.
It is 75 million light-years away, and according to observations, these galaxies reside in smaller groups that are gravitationally linked to each other.
Other Deep-sky Objects In Eridanus:
- NGC 1535 is a small blue-gray planetary nebula visible in small amateur telescopes, with a disk visible on large amateur instruments. At 2000 light-years away, it is of the ninth magnitude.
- IC 2118: It is a faint reflection nebula thought to be an ancient supernova remnant or a cloud of gas illuminated by the nearby supergiant star Rigel in Orion.
- NGC 1232, NGC 1234, and NGC 1291 are three large spiral galaxies of luminosity in the constellation Eridanus.
- NGC 1300: It is a barred spiral galaxy of great design.
- NGC 1300 is a barred spiral galaxy located 61 (about 8) million light-years away. The center of the bar shows an unusual structure: within the overall spiral structure, there is a significant design spiral that is 3,300 light-years in diameter. Its spiral arms are tightly wound.
Meteor Showers


Within the boundaries of the constellation Eridanus, there are at least two newly discovered meteor showers.
The most notable is the "Nu Eridanids," visible between August 30 and September 12 of each year.
The second is the "Omicron Eridanids," which reaches its peak exposure point between November 1 and 10.
Conclusions
- Eridanus is a constellation located primarily in the southern hemisphere. The constellation's name comes from Greek history and means "Lesser River."
- The constellation Eridanus is located primarily in the southern celestial hemisphere. It is associated with a history of Babylonian culture over a single city, although it may also have been associated with the Eridanus River.
- The constellation Eridanus is the sixth-largest of all, covering an area of 1,138 square degrees.
- The best month to see the Eridanus constellation is in December, between the latitudes of 32° N and 90° S.
- The easiest way to locate the constellation Eridanus is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the constellation Phoenix to the constellation Reticulum; in the middle of the road between the two, you will find the star Achernar, the brightest of the constellation Eridanus, from there you can find the rest of the constellation.
- The brightest star in the constellation Eridanus is Achernar (Alpha Eridani / α Eri / HR 472 / HIP 7588), with an apparent magnitude of +0.45.
- The most notable deep-sky body of the constellation Eridanus is the galactic Cumulus of Eridanus, containing at least 200 galaxies.
- The most notable shower of stars in the constellation of Eridanus is the "Nu Eridanids," which has its maximum exposure date between August 30 and September 12 of each year.






