Taurus Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Taurus (The bull)
Taurus is one of the zodiac constellations; it is also the 17th largest and one of the oldest in the historical records of different cultures such as Babylon or Greek.
It is located in the northern hemisphere and has a Y shape. It also contains one of the brightest stars of all, Aldebaran, an orange giant that is easy to find in the sky.
Its name comes from the Latin "Taurus," which means Bull.
From May 14 to July 21, it is impossible to see this constellation since the Sun passes right in front of it. For the rest of the year, the constellation is visible.

The Mythology And History Of The Taurus Constellation
Ancient Egypt


It is believed that the Egyptians were among the first civilizations to record the constellation of the zodiac in the famous Dendera Zodiac, which is more than 2,000 years old.
For the Egyptians, the constellation of Taurus meant strength and fertility. That is why they represented him with the figure of Osiris (God who had a half-bull body) and Isis (God who had a half-cow body).
In addition, this constellation indicated the dates when the Nile River began to rise. Thus they knew when to stop cultivating and rest until the level of the river dropped.
Greek Mythology


According to Greek mythology, Zeus took the form of a bull to seduce the Phoenician princess Europa, with whom he had three children: Minos, Sarpedon and Rhadamanthys.
Thanks to this, the constellation was assigned the figure of the minotaur, which represents Zeus transformed into a Bull.
Early Modern Period


During the 17th and 18th centuries, astronomers such as Copernicus used the constellation of Taurus to determine the distances of celestial bodies and begin to measure the universe.
Many astronomers used the star Aldebaran as a reference to locate other nearby celestial bodies. At the same time, due to its orange glow, it served as an indicator to compare it with other stars that had the same color.
Centuries ago, people thought that if two stars were the same color, they were also the same size. Although this statement is not entirely correct, it was of great help to estimate the first measurements of the observable universe using the stellar parallax method.
Nowadays


As in the rest of the constellations, Taurus continues to give us some surprises, such as the recent discovery made by the team of astronomers of Dr. Tereza Jerabkova, a researcher at ESA (European Space Agency).
Scientists analyzed the star mapping satellite Gaia data, discovering that some stars in the "Hyades" star cluster are "fading".
According to observations, an object ten million times more massive than the Sun in the constellation Taurus alters the movements and trajectories of the star cluster, causing the group to run out of stars gradually.
Calculations indicate that there could be a subhalo of dark matter in this region that gravitationally influences nearby stars.
How To Find The Taurus Constellation?
Visibility By Region
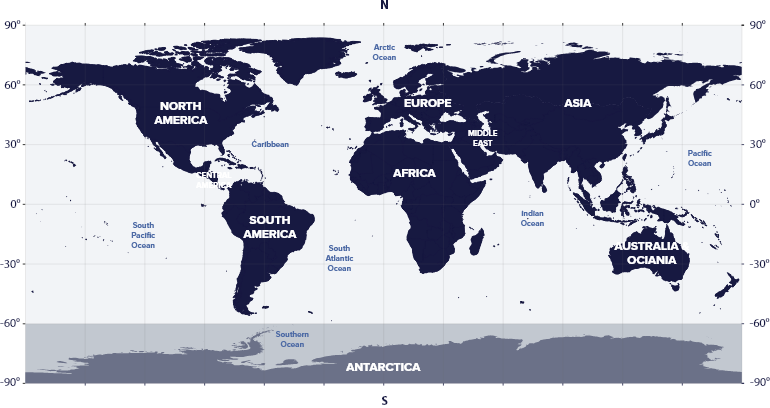

Taurus is a constellation found mainly in the northern hemisphere. However, it is also visible in southern countries.
It is visible in America, Europe, Asia, Oceania, and Africa, but not Antarctica.
Visibility by season
Taurus is a seasonal constellation, so it is only visible between July 21 to May 14, that is, in the autumn, winter, and summer seasons of the Earth's northern hemisphere. Constellation is not visible from May 14 to July 21 because the sun crosses it.
The best time to see the constellation is in winter due to the climate to observe its brightness better.
Finding Taurus Constellation
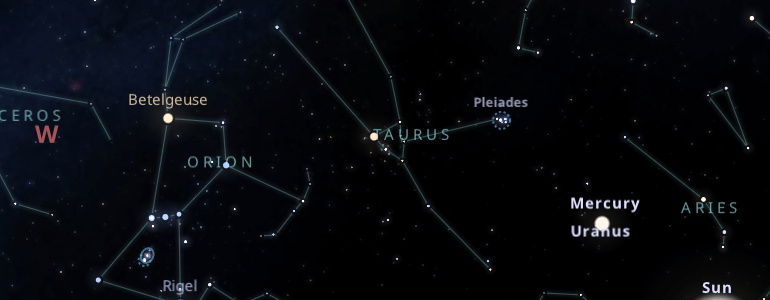

To find the constellation of Taurus, you must look along the ecliptic, between the constellations of Orion and Aries. You have to find the V-shaped star pattern that resembles the horns of a bull.
Another way to locate it is through the star Aldebaran. First, you have to find the orange star closest to the zenith, and then a set of V-shaped stars, the stellar set Hyades that belongs to Taurus.
If you have telescopes or binoculars, you will have to locate them using the coordinates 58° S and 89° N.
Related Constellations
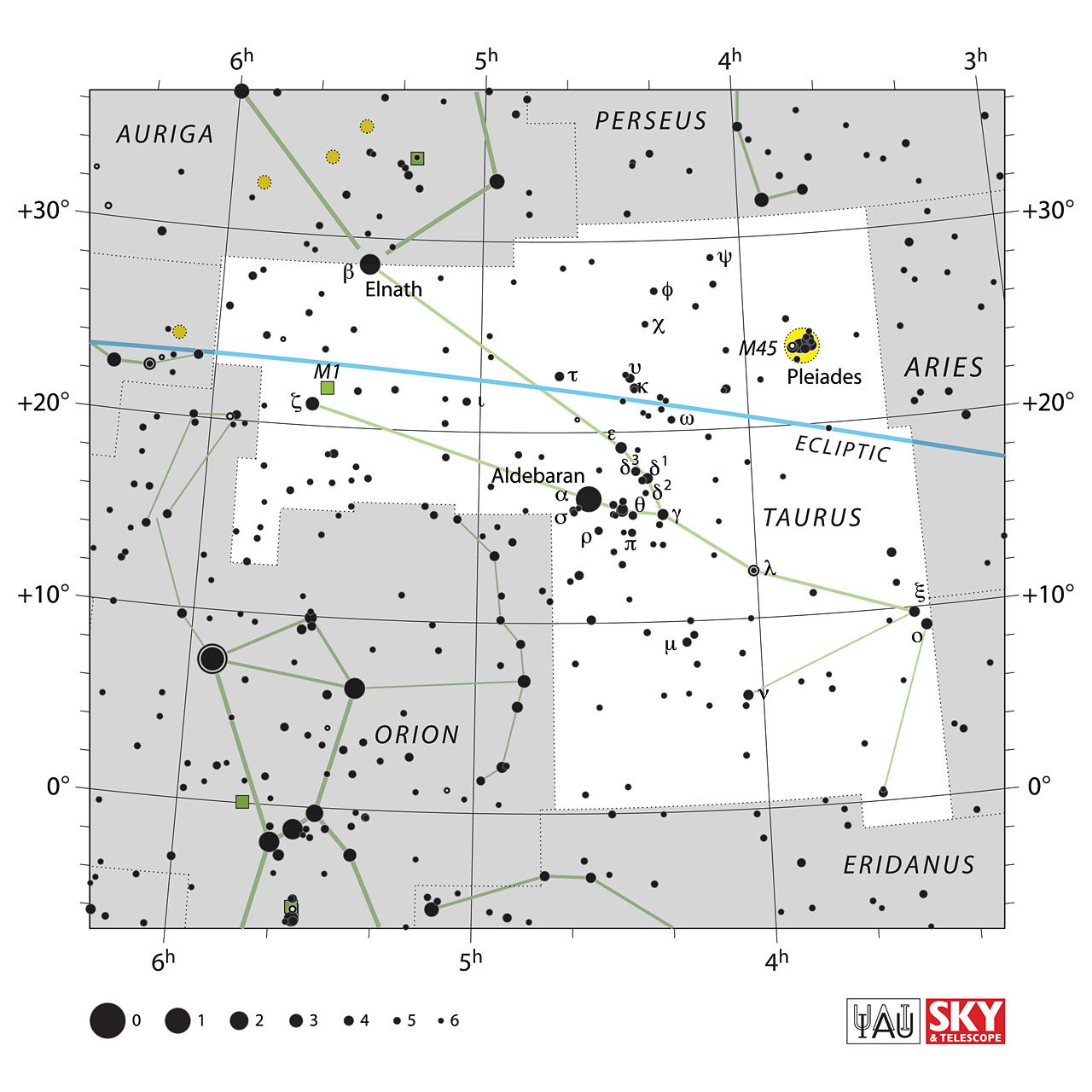

Stars in Taurus Constellation
Officially the constellation of Taurus contains 223 stars; however, most of them can only be seen with telescopes since they have a magnitude less than 6.5.
Forty of them are part of "Main Stars".
Five are the ones that make up the figure associated with the Bull:
Aldebaran (α Tauri)
An orange giant star 44 times bigger than the Sun; it is the brightest of the entire constellation of Taurus. Its name comes from the Arabic "aldubran," which means "The one that follows," because seen from the Earth, the star seems to chase the Pleiades in its journey through the sky.
Alnath (β Tauri) and Zeta Tauri (ζ Tauri)
Together, they form the horns of the Bull.
Alnath is a bluish-white giant and the second brightest star in the entire constellation of Taurus. According to measurements, it is 700 times brighter than the Sun.
On the other hand, Zeta Tauri is an eclipsing binary star of a blue giant with nine solar masses and a much less bright red dwarf.
Lambda Tauri (λ Tauri)
Like Zeta Tauri, it is an eclipsing binary star made up of a giant blue star 4000 times brighter than the Sun and a white subgiant 95 times brighter than the Sun.
Ushakaron (ξ Tauri)
A quadruple star system made up of a triple system on which a fourth-star orbits, which takes a century to complete its orbit around the other stars.
T Tauri
Like ξ Tauri, it is not a single star, but rather a triple star system, made up of a main yellow-orange star only 1 million years old, while the other two stars only can be seen in the infrared and it is unknown at what stage they are.
Other Taurus Stars:
- γ Tauri (Hyadum I): Located 152 light-years and with a brightness of 79 suns, this orange giant star is part of the Hyades star cluster.
- δ Tauri: Consists of a triple star system located 153 light-years away, consisting of an orange giant and two white dwarfs. They are all part of the Hyades star cluster.
- δ1 Tauri (Hyadum II): It is a star very similar to Hyadum I.
- ε Tauri (Ain): A part of the Hyades star cluster located 155 light-years away. This orange-yellow giant star has an exoplanet orbiting around it.
- η Tauri (Alcíone): A bluish-white young star and the third brightest star in the constellation; It is located 440 light-years from the solar system and is the brightest in the Pleiades cluster.
- θ Tauri: This star is two different stars, θ1 Tauri of orange color and θ2 Tauri of white paint; both stars are part of the Hyades.
Other stars that are part of the main group:
- κ Tauri
- ν Tauri
- ο Tauri
- π Tauri
- ρ Tauri
- ω2 Tauri
- n Tauri
- Merope (23 Tauri)
- 10 Tauri
- 30 Tauri (e Tauri)
- 39 Tauri
- 79 Tauri
- 90 Tauri (c Tauri)
- 111 Tauri
- 139 Tauri
- T Tauri
- Y Tauri
- RV Tauri
- RZ Tauri
- UX Tauri
- AA Tauri
- CD Tauri
- CE Tauri (119 Tauri)
- DG Tauri
- EQ Tauri
- IK Tauri (NML Tauri)
- HD 37124
- Gliese 176 (HD 285968)
- CoKu Tauri/4
- Gliese 169
- HL Tau 76 (V411 Tauri)
Deep Sky Objects


M45 (THE PLEIADES)
It is one of the most famous objects not only in the constellation of Taurus but in the entire sky. This star cluster is one of the most recorded throughout history. Its brightest stars are all blue, which gives it an unmistakable appearance.
This star cluster is located 444 light-years away, making it one of the closest star clusters to Earth and estimated to have between 500 and 1000 stars.
HYADES
This cluster of stars is only 152 light-years away, making it the closest to Earth; therefore, it has been the most studied cluster to date.
It contains 80 stars, of which the brightest make up the head of Taurus.
M1 (CRAB NEBULA)
Formed by the death of a star in 1054, this planetary nebula is actually a supernova remnant.
Inside the star, we can find a pulsating star, better known as a neutron star, which emits vast amounts of radiation towards the outer gases of the nebula.
NGC 1514
On November 13, 1790, the famous astronomer William Herschel discovered this planetary nebula located 600 light-years away.
NGC 1555
This nebula is a Herbig-Haro object, a recently formed nebula with a short life of thousands of years.
SIMEIS 147 (Spaghetti Nebula)
At approximately 140,000 years old, this nebula is a supernova remnant and one of the galaxy's most evolved.
It was discovered in 1952 by the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Simeiz and is located about 3,261.56 light-years from the solar system.
NGC 1410 and NGC 1409
They are two galaxies interacting in a cosmic dance where they will merge into one.
Meteor Shower


The constellation of Taurus is associated with a shower of stars, called the Taurids, and this meteor shower takes place from the beginning of November to the middle of the same month.
To find this constellation, you can look to the right towards the Pleiades star cluster to find this constellation. Thanks to the remnants of ice left by Comet 2p / Encke, this meteor shower occurs.
Interesting Facts
- Taurus is one of the most studied constellations throughout history due to its visibility in both hemispheres. Due to this, this was where the first investigations of star clusters and extrasolar planets began.
- Currently, Taurus is one of the constellations that houses one of the most significant numbers of binary stars and stars with exoplanets.
- Some of the stars that make up the constellation Taurus contain very Earth-like planets like Gliese 176.
Conclusions
- Taurus is one of the most critical and famous constellations in history because it is large and bright; thanks to that, it is relatively easy to find because you only need to locate the only star cluster that contains seven blue stars the Pleiades.
- Being a zodiac constellation, it is visible on all continents except Antarctica.
- It is a seasonal constellation and cannot be observed all year long. It is visible in Autumn and winter, but the best time to see it is in January.
- Its brightest star, Aldebaran, has been recorded for millennia, and its orange glow makes it very easy to recognize.
- We can find many deep-sky objects in its vicinity, such as the famous crab nebula.
- Its name comes from the bull, the creature that Zeus was transformed into in Greek mythology.
Sources Of Information
- https://www.constellation-guide.com/constellation-list/taurus-constellation/
- https://earthsky.org/astronomy-essentials/taurus-heres-your-constellation/
- https://www.space.com/17101-taurus-constellation.html
- http://www.seasky.org/constellations/constellation-taurus.html
- https://egyptianmuseum.org/explore/greco-and-roman-period-monuments-dendera-zodiac






