Scorpius Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Scorpius (The scorpion)
Scorpius is one of the 12 constellations of the zodiac. In Latin, the constellation Scorpius means "the scorpion," and the Scorpio's story comes from Greek mythology.
The location of the constellation Scorpius is essentially in the southern hemisphere. In the northern hemisphere, we can find it in the night sky throughout the summer and in the southern hemisphere in the winter.
The constellation of Scorpius is the easiest to see in the night sky because it is one of the brightest constellations and is J-shaped.
The brightest stars of Scorpius are Antares - α Scorpii (Alpha Scorpii), Shaula - λ Scorpii (Lambda Scorpii), Sargas - θ Scorpii (Theta Scorpii).
Scorpio's constellation is home to deep-sky objects such as galaxies, nebulas, and star clusters. In addition, within the constellation's boundaries, there are occurrences of several meteor showers.

The Mythology And History Of The Scorpius Constellation
Ancient Egypt


In ancient Egypt, Scorpio's constellation was associated with the God escorpión Serket (From the Greek "The one who makes the throat breathe").
n the earliest records of Egyptian culture, the constellation Scorpius was associated with a snake, not a scorpion.
But the Dendera Zodiac constellation was depicted as a scorpion and not a serpent.
Sometime later, the serpent soon obtained its constellation, which we know today as the Serpens constellation, from the Latin "Serpens," which means snake.
Greek Mythology


In Greek mythology, the story goes that Orion the Hunter boasted of his excellent hunting skills. He said that there was no animal on Earth that he could not hunt.
Then Gaia, the goddess of the Earth, and all animals sent a giant scorpion to sting Orion, killing him.
This is how Scorpius and Orion became mortal enemies. Zeus, the father of it all, decided to place Orion and the Scorpion in the heavens to commemorate their battle, but in such a way that the two enemies will never meet.
That is why, according to the myth, it is not possible to see these two constellations together at the same time because when one comes out, the other leaves.
Early Modern Period


From its designation by the astronomer Ptolemy to the present day, the constellation Scorpius remained under its original name.
On the contrary, its borders have undergone alterations as it is a larger than average constellation, like the case of the scorpion's tweezers.
At first, the constellation of Libra was the tweezers of the scorpius, but over time, Libra became considered an independent constellation; hence its name is related to the claws of the scorpion.
Nowadays


Recently Dr. Javier de Cos of the University of Oviedo, in conjunction with a team of researchers from the Astrophysical Institute of the Canary Islands, discovered that one of the stars in the constellation of Libra has an exoplanet (a planet that is orbiting a star other than the Sun).
The discovery was carried out with the Kepler space telescope and the OSIRIS modules of the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) and HARPS-N of the Galileo National Telescope (TNG).
It is located at a distance of 244 light-years away. This star has 0.62 of the radius of the SunSun and a temperature of only 3650º C, so it can be said that it is much smaller and colder.
The exoplanet has 2.1 times the radius of the Earth and, according to the survey, could have a temperature between 40º C and 60º C, so it could have liquid water, which makes it a significant candidate to host earthly life.
How To Find The Scorpius Constellation?
Visibility By Region
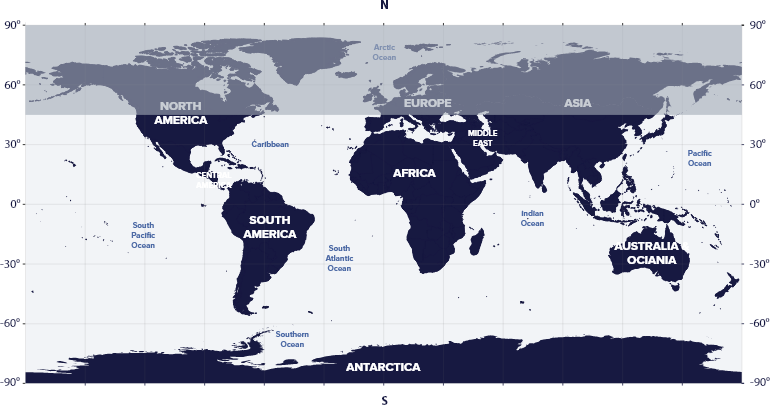

Scorpio resides in the third quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (SQ3) between 90° S and 44° N. We can see the constellation in the night sky from the Southern and some parts of the Northern hemisphere.
In the Northern Hemisphere, you cannot see Scorpio in the areas north of New York, Spain, and China.
Visibility By Season
Scorpio is a seasonal constellation, which means it cannot be seen in the sky all year round. It belongs to the group of northern summer constellations and southern winter constellations.
We can see it from the end of June to September.
The best month to observe this constellation is July.
Finding Scorpius Constellation
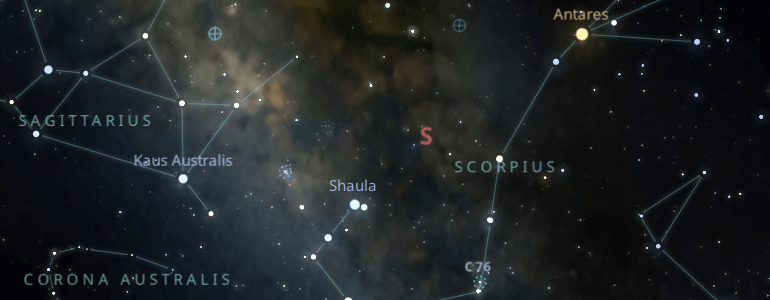

Scorpio is a very bright constellation, so you will have no trouble finding it.
An easy way to do this is by locating the star Kaus Australis in the very bright constellation Sagittarius and then drawing a line to the constellation Libra.
In the middle is the star Antares, which belongs to Scorpius and is distinguished because it is one of the brightest in the entire sky.
Remember that Scorpio is shaped like a hook or the letter J.
Scorpio's brightest star is Antares, or Ant-ares, the "rival of Mars," and you can see it in the center of the constellation during the summer season.
Related Constellations
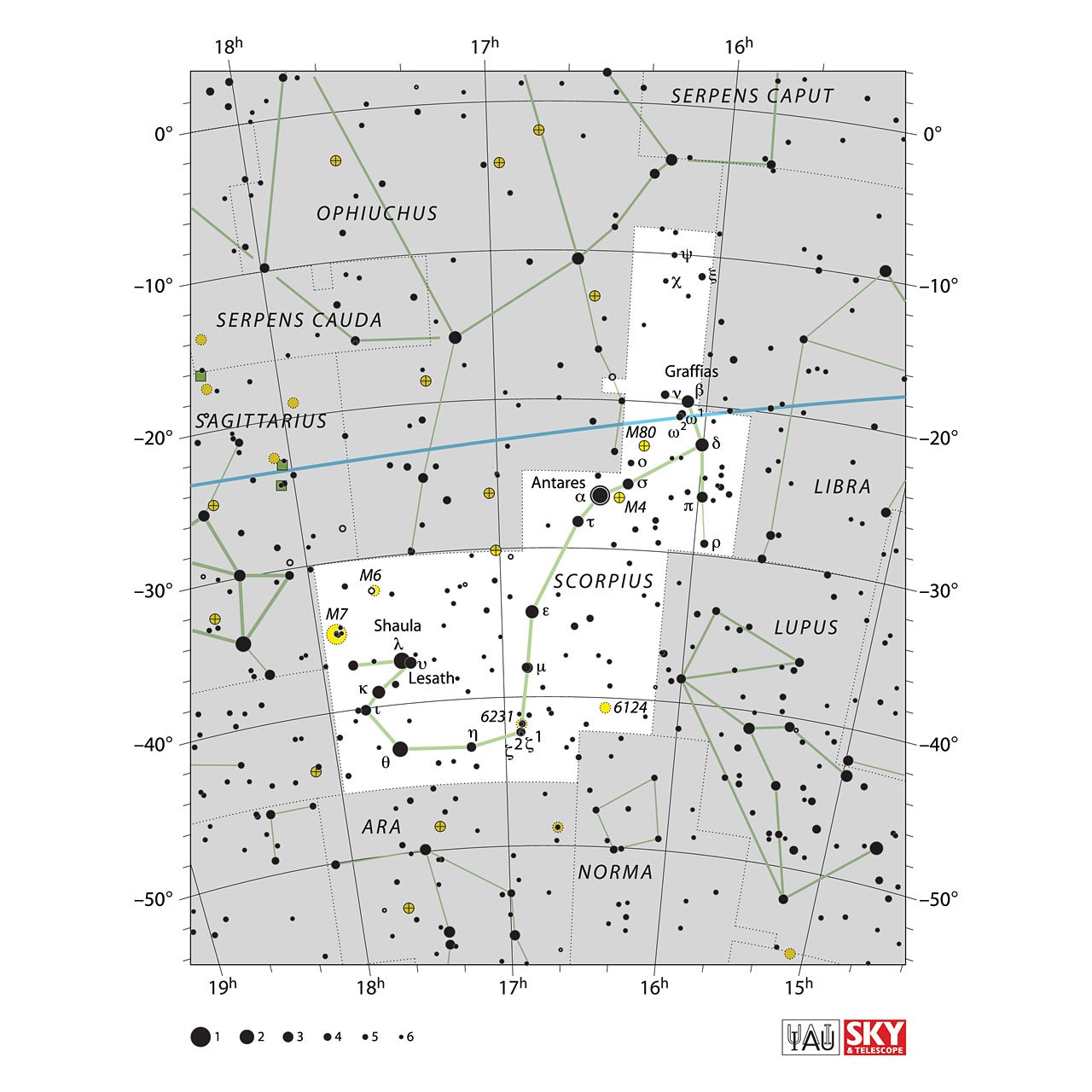

Stars in Scorpio Constellation
The brightest stars of Scorpio are Antares - α Scorpii (Alpha Scorpii), Shaula - λ Scorpii (Lambda Scorpii), Sargas - θ Scorpii (Theta Scorpii).
Officially Scorpius has 167 stars in its region, of which 18 have proper names designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These stars are Acrab, Alniyat, Antares, Dìwö, Dschubba, Fang, Fuyue, Iklil, Jabbah, Larawag, Lesath, Paikauhale, Pipirima, Rapeto, Sargas, Sharjah, Shaula and Xamidimura.
There are also several binary stars within this constellation: the 2-star systems. In addition, Scorpius encompasses variable stars that change their magnitude (brightness) during the year and stars with planetary systems.
Antares - α Scorpii (Alpha Scorpii)
Antares is a red supergiant of class M1.5Iab. It is the brightest star in the constellation of Scorpio and the sixteenth brightest in the entire night sky with the most apparent magnitude +1.09.
Located approximately 550 light-years from Earth, it approaches our solar system at a speed of 3.4 km/s.
In addition, it is 10,000 times more luminous than the Sun, with a surface temperature of 3600 K and its radius of 883 sun radius.
Shaula (λ Sco / 35 Sco)
Shaula is the second brightest star in Scorpio's constellation. It has three main components: λ Scorpii A, λ Scorpii B, and λ Scorpii C.
In turn, λ Scorpii A is a triple star system whose components are a blue giant star(Shaula Aa)accompanied by a neutron star(Shaula Ab).
Twills (Theta Scorpii / θ Sco / HD 159532)
Also known as Girtab and located at a distance of 270 light-years from the Solar System, Sargas is the third brightest star in the constellation of Scorpius.
Sargas is a white-yellow luminous giant of spectral type F1II with an apparent magnitude of +1.86 and a surface temperature of 7200 K.
It has a radius 20 times greater than the solar radius and a luminosity9 60 times greater than that of the Sun.
In addition, it is a rotating star with a rotational speed of 105 km/s and completes one turn every ten days.
Gliese 667 (GJ 667 / HD 156384 / HR 6426 / MLO 4)
Located 22 light-years from Earth, Gliese 667 is a triple star system, where Gliese 667 C orbits around the inner pair formed by Gliese 667 A and Gliese 667 B.
This star is famous because it contains at least six super-Earth exoplanets, that is, planets very similar to ours. Three are in the habitable zone of the star system.
It is the most promising planetary system to find life outside the Earth since it has three planets in which there may be water in a liquid state.
In proximity to the star, the planets are Gliese 667C b, h (not confirmed), c, f, e, d, g.
OTHER SCORPIUS STARS:
- δ Scorpii
- ε Scorpii
- ζ1 Scorpii
- η Scorpii
- ι1 Scorpii
- ι2 Scorpii
- λ Scorpii
- κ Scorpii
- ξ Scorpii
- μ1 Scorpii
- ο Scorpii
- π Scorpii
- ρ Scorpii
- σ Scorpii
- τ Scorpii
- υ Scorpii
- G Scorpii
- k Scorpii
- Q Scorpii
- 18 Scorpii
- U Scorpii
- BM Scorpii
- FV Scorpii
- AH Scorpii
- V856 Scorpii (HR 5999)
- V1075 Scorpii
- HD 144432 (Hen 3-1141)
- HD 145825
- HD 147513
- Gliese 682
- HIP 7943
- 1RXS J160929.1-210524
- Pismis 24-1 (HD 319718)
- HD 160529
- HD 1494
Deep-sky Objects
Scorpio is also known as the home of several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies), or galaxies.
In the case of Scorpio, it is rich in several nebulae and star clusters. The most famous with better visibility are:
Globular cluster M4 (Messier 4 or NGC 6121)
Discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in the year 1746, this was the first globular cluster where the naked eye distinguished individual stars.
It is at a distance of only 7200 light-years.
It has at least 43 variable stars within its borders, and it is possible to distinguish them with an amateur telescope.
Open ClusterM6, (Messier 6 or NGC 6405)
With an apparent magnitude of 4.48, M6 is an open cluster of hot, young stars of spectral types O and B.
It is located 1600 light-years from the solar system. Its radial velocity is -11.50 km / s, and calculations indicate that it approaches the Earth at about 41 400 km / h.
NGC 6302 e (Insect Nebula)
Located at 3400 light-years from the Sun, NGC 6302 is one of the most complex planetary nebulae known and famous.
Multispectral analyses indicate that it has a central star with a temperature of 200,000 K, making it one of the hottest objects in the universe.
Other Deep-sky Objects:
- M6
- M7
- M80 (globular cluster)
- Open cluster NGC 6124
- Open cluster NGC 6231
- Remnants of supernova CTB 37A
- G350.1-0.3 (Supernova remnant)
- Tornado Nebula
- Cotton Candy Nebula
Meteor Showers


A meteor shower is within the constellation's boundaries called "Alpha Scorpiids."
This occurs between April 21 and May 26, and its maximum exposure occurs on May 15 of each year.
Interesting Facts
- In Hawaii, Scorpius is known as the Maui demigod hook Hawaii because of the similarities.
- Scorpius remained divided into two asterisms that sailors used for navigation. The northern part is called bintoéng lambarué, meaning "skating stars" and the southern part is called bintoéng balé mangngiwéng, meaning "shark stars."
- The Javanese town of Indonesia calls the constellation Scorpio Banyakangrem ("the hatched swan") because its shape resembles a swan's neck.
Conclusions
- Since Scorpius is a zodiac constellation, it belongs to the zodiac family's constellations.
- Scorpius means "the scorpion," derived from Greek mythology. Orion the Hunter boasted of his excellent hunting skills, and Gaia, the goddess of the Earth, sent a considerable scorpion to sting Orion, killing him on the spot.
- Scorpius is a southern constellation, but we can see it from some countries in the northern hemisphere. The best time to observe Scorpius is July.
- Scorpius is easy to locate since it has very bright stars like Antares, one of the brightest stars in the entire sky.
- Scorpio is visible from North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, And Antarctica.
- The only exceptions are far north, from New York, Spain, and China.
- The brightest star in the constellation is Antares. It is one of the five most brilliant stars in the night sky, with a visual magnitude of 0.96; it is 10,000 times more luminous than the Sun and is 550 light-years away.
- The most notable nebula within the borders of Scorpius is NGC 6302, better known as the Butterfly Nebula.
- The strongest meteor shower in Scorpius is the "Alpha Scorpiids."






