La constelación Canis Maior: La guía definitiva
Canis Maior (Can Mayor)
Canis Maior es una de las constelaciones más grandes y prominentes del hemisferio sur celeste. El nombre de la constelación proviene del latín y significa "perro mayor".
La ubicación de la constelación Canis Maior está esencialmente en el hemisferio sur, pero es posible visualizarla en la mayoría de países del hemisferio norte y podemos encontrarlo en el cielo nocturno durante todo el invierno.
La constelación Canis Maior es una de las más fáciles de ver ya que contiene a la estrella más brillante del cielo nocturno, Sirio, la cual tiene una magnitud aparente de 1,46.
La constelación de Canis Maior es el hogar de objetos de cielo profundo como las galaxias, nebulosas y cúmulos estelares.
No hay ocurrencias de lluvias de meteoros dentro de los límites de la constelación.

La Mitología Y La Historia De La Constelación De Canis Maior
Antiguo Egipto


The constellation Canis Major contains Sirius, the brightest star in the sky. Because of this, Sirius has been present in records since prehistoric times in mythology, religions, and customs of numerous cultures.
In Ancient Egypt, the star Sirius was known as Sopdet, Sothis, or Sethis and is symbolized by a dog. Hence the name "The Older Dog" will be recognized later.
Canis Major was the most critical constellation for those who studied astronomy in the past since the famous astronomer Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria used the star Sirius as the location of the earth's central meridian.
Mitología Griega


In Greek mythology, the constellation Canis Major has several associated histories; however, influencing previous cultures, all the stories were related in some way to a dog.
In one such story, Canis Major depicts the dog Laelaps, a gift from Zeus to the Phoenician princess Europa.
The constellation was more popularly associated with one of Orion's hunting dogs, chasing Lepus, a hare impossible to hunt as it was too fast.
Era Moderna


In the modern period, Canis Major was relevant in the trade and navigation of Europe as explorers venturing east used this constellation as a reference point to travel through the desert at night.
In addition, during the boreal summer, the star Sirius is invisible or instead hidden from view, because of this, the astronomers of antiquity thought that the energy of Sirius was added to that of the Sun to produce the hottest days of the year or "can days,” better known today as "canicular days.”
En La Actualidad


Canis Major remains one of the most colorful and imposing constellations due to its excellent brightness.
Although it has been one of the most cataloged constellations throughout history, it has undergone very few modifications in its boundaries. It remains one of the brightest in the sky.
Canis Major is a medium-sized constellation. It covers an area of 380 square degrees in the celestial vault and ranks 43rd in size among the 88 constellations in the night sky.
Canis Major is a region teeming with deep space bodies of paramount importance to science and astronomy in scientific research.
¿cómo Encontrar La Constelación De Canis Maior?
Visibilidad Por Región
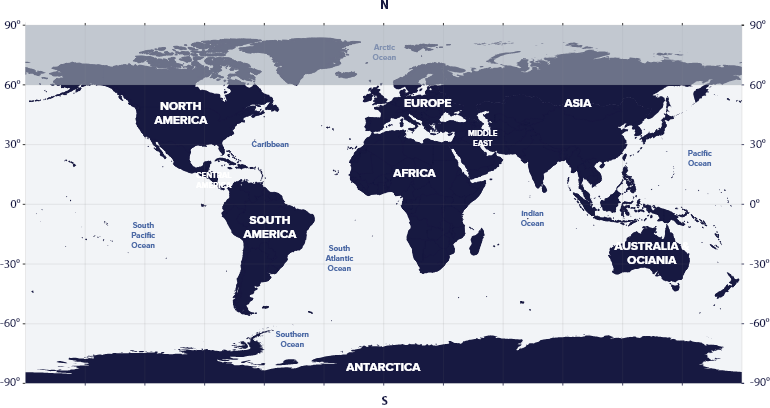

Canis Major resides in the first quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (NQ1) at latitudes between 60° N and 90° S. We can see the constellation in the night sky from all countries of the southern hemisphere of the earth and some countries of the northern hemisphere.
Canis Major is visible in America, Europe, Asia, Australia, and Antarctica.
Canis Major is not visible in areas above 60° N latitude, such as Finland, northern Norway, northern Sweden, northern Greenland, northern Canada, and Alaska.
Visibilidad Por Temporada
Canis Major is a constellation that can be seen most of the year because it is relatively close to the equator; however, February is the best month to see it.
In the northern hemisphere, the Canis Major constellation is visible during the winter. In contraste, the Canis Major is visible during the summer in the southern hemisphere.
¿cómo Encontrar A Canis Maior?
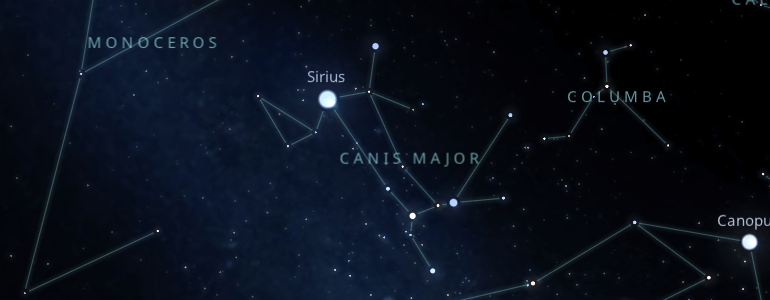

Depending on which hemisphere of the earth you are from, Canis major will be seen in different moments of the year and at different times of the day.
If you are in the northern hemisphere, you should look for it on the horizon, always looking south. In the southern hemisphere, you should look up near the Zenith.
The easiest way to locate the constellation Canis Major is to locate the brightest blue star in the sky, Sirius, a bluish-white star brighter than any other star but not as bright as a planet.
Canis Major is located right between the constellations of Monoceros and Columba.
Constelaciones Relacionadas
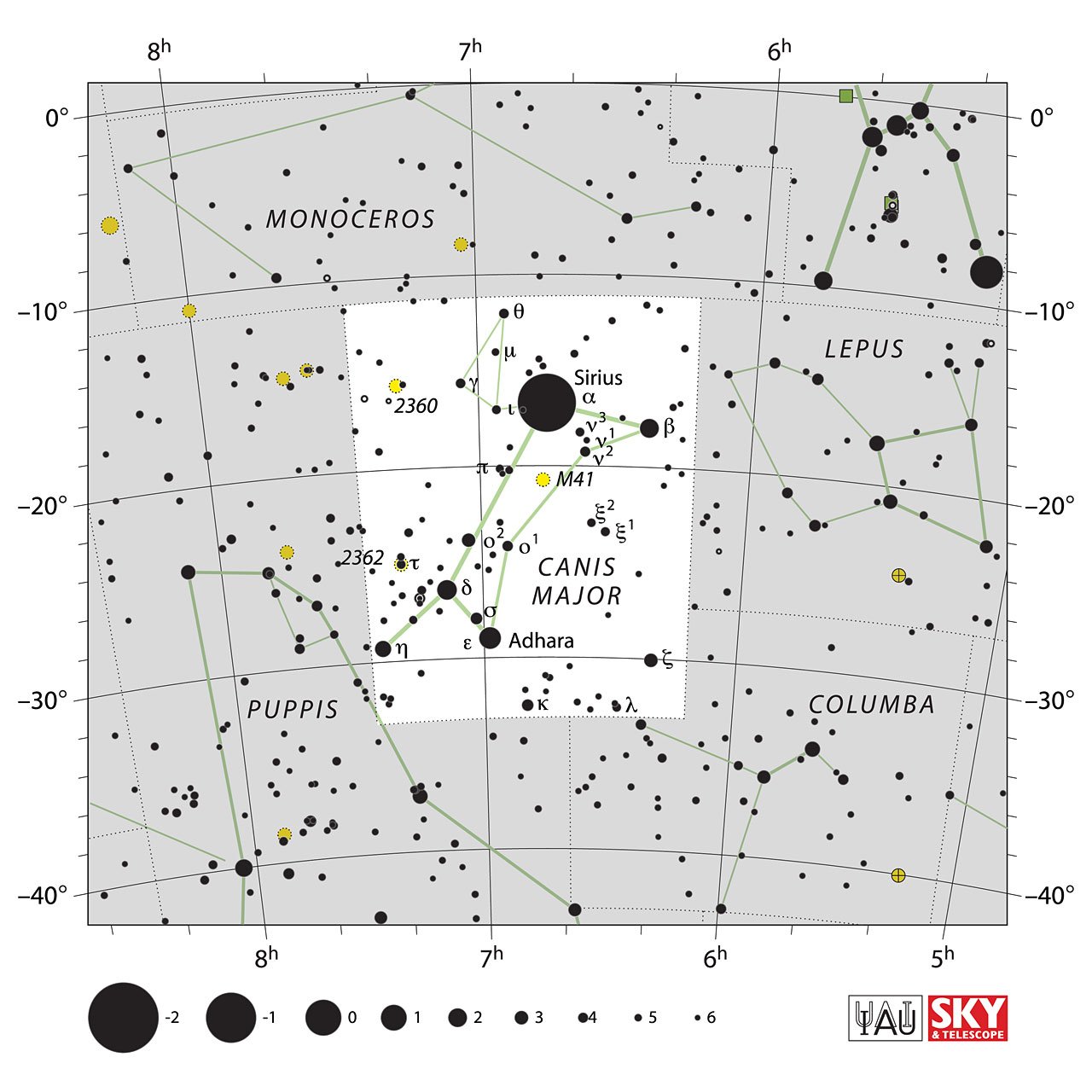

Estrellas En La Constelación De Canis Maior
The constellation Canis Major has 147 stars officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union, of which 10 form the central figure of the constellation, are they Sirius, Adhara, Wezen, Mirzam, Aludra, Furud, Kappa Canis Major, Theta Canis Major, Muliphen, and Iota Canis Major.
Sirius (Sirius / Alpha Canis Maioris / α CMA)
Sirio is Canis Major's brightest star with an apparent magnitude of -1.46; it is a blue-white giant star that lies only 8.6 light-years from Earth, the seventh closest star to the sun.
Sirius is a binary star system of Sirius A, Sirius B. Sirius A is a white main-sequence star. Sirius B is a white dwarf with a mass very similar to the sun but the same size as the earth.
Adhara (Epsilon Canis Majoris / ε CMa / 21 Canis Majoris)
With an apparent magnitude of +1.51. Adhara is the second brightest star in the constellation Canis Major. It is located 405 light-years from the solar system.
Wezen o Wesen (Delta Canis Majoris / δ CMa / 25 Canis Majoris)
Wezen is the third brightest star in the constellation Canis Major with a magnitude of 1.83; it is one of the giant yellow supergiant stars observables to the naked eye. It is located 1800 light-years from the earth.
Otras estrellas notables en la constelación Canis Maior:
- β Canis Maioris (Murzim o Mirzam): Con magnitud 1,98 Murzim es una estrella gigante azul y variable del tipo Beta Cephei.
- ζ Canis Maioris (Furud), binaria espectroscópica de magnitud 3,02 y color blanco-azulado.
- η Canis Maioris (Aludra): Con una magnitud de 2,45, Aludra es una supergigante azul tan luminosa como 66.000 soles y variable de tipo Alfa Cygni.
- θ Canis Maioris: Es una estrella gigante naranja de magnitud 4,09.
- ι Canis Maioris: Es una estrella supergigante azul 46.000 veces más luminosa que el Sol.
- κ Canis Maioris: Estrella Be de magnitud 3,51.
- μ Canis Maioris: Estrella binaria fija cuyas dos componentes se hallan separadas 3 segundos de arco.
- ν Canis Maioris: Es una estrella triple a 65 años luz que contiene una subgigante naranja con dos planetas extrasolares.
- ξ Canis Maioris: Es una estrella binaria conformada por ξ1 Canis Maioris, una subgigante azul, y ξ2 Canis Maioris, una gigante blanca.
- ο Canis Maioris: Estrella binaria conformada una supergigante naranja llamada ο1 Canis Maioris y ο2 Canis Maioris, una supergigante azul.
- π Canis Maioris: Es una estrella con un disco circunestelar de polvo.
- σ Canis Maioris: Estrella supergigante roja cuyo brillo varía entre magnitud 3,43 y 3,51.
- τ Canis Maioris: Estrella supergigante del raro tipo espectral O, la más brillante del cúmulo NGC 2362.
- ω Canis Maioris: Es una estrella azul y variable eruptiva Gamma Cassiopeiae.
- 12 Canis Maioris (HK Canis Maioris): Estrella de magnitud 6,08.
- 15 Canis Maioris (EY Canis Maioris): Supergigante blanco-azulada de magnitud 4,81.
- 26 Canis Maioris (MM Canis Maioris): Estrella tipo Bp de magnitud media 5,90.
- 27 Canis Maioris (EW Canis Maioris): Es un sistema estelar triple.
- R Canis Maioris: estrella binaria cercana y binaria eclipsante de magnitud 5,71.
- Z Canis Maioris: Es un sistema binario compuesto por una estrella Herbig Ae/Be y una estrella FU Orionis.
- SW Canis Maioris: Estrella binaria eclipsante de magnitud 9,15.
- VY Canis Maioris: Es una de las estrellas hipergigantes más grandes conocidas y una de las más luminosas.
- FR Canis Maioris: Estrella variable tipo Be.
- FW Canis Maioris: Estrella variable tipo Gamma Cassiopeiae.
- EZ Canis Maioris: Estrella Wolf-Rayet.
- FZ Canis Maioris: Es un sistema triple de magnitud 8,14.
- NR Canis Maioris: Variable Delta Scuti de magnitud 5,62.
- HD 45184: Estrella similar al sol con una magnitud 6,37 ubicada 72 años luz.
- HD 47536 (HR 2447): Estrella gigante naranja con dos planetas extrasolares.
Objetos Del Espacio Profundo


Canis Major is also known as the home of several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies), or galaxies. In the case of Canis Major, he is rich in several notable galaxies.
M41 (NGC 2287)
The most notable deep sky body of Canis Major is the stellar cumulus M41 (NGC 2287); this is an open cumulus made up of 100 stars, is located 2300 light-years from earth, and was recorded by Aristotle from 325 BC.C.
Otros cuerpos de espacio profundo notables en Canis Maior:
- NGC 2362: Es un cúmulo abierto compuesto por unas 60 estrellas; el cumulo tiene una edad estimada entre 4 y 5 millones de años.
- NGC 2359: Mejor conocida como nebulosa del Casco de Thor debido a su forma recuerda al casco de un guerrero. Es una nebulosa de emisión iluminada por la estrella de Wolf-Rayet WR 7.
- NGC 2280: La galaxia más brillante de la constelación Canis Maior, es una espiral barrada situada al noroeste de de la estrella Adhara.
- NGC 2217: Es una galaxia espiral barrada que se encuentra al norte de de la estrella Furud.
- NGC 2207: Es una galaxia espiral barrada de magnitud 10,8.
- IC 2163 y NGC 2207: Son dos galaxias espirales en interacción que se están fusionando, se encuentra aproximadamente a 80 millones de años luz de nuestra galaxia.
- Galaxia Enana del Can Mayor. También clasificiada como una galaxia irregular, se considera la galaxia más cercana a la Vía Láctea, situada a solo 25 000 años luz de distancia.
Datos Interesantes
- Canis Maior tiene asociada una gran variedad de historias diferentes, pero en todas siempre se le asocia con la figura de un perro.
- A diferencia de la mayoria de las constelaciones del hemisferio sur, Canis Maior es una constelación que tiene registros desde hace miles de años.
Conclusiones
- Canis Maior es una constelación ubicada en el hemisferio sur de la tierra
- El nombre de la constelación Canis Maior proviene del latín y significa "perro mayor".
- Canis Maior es una constelación del sur, pero es posible verla desde todos los países del hemisferio norte, solo deja de ser visible en aquellas regiones por encima de los 60° N.
- Canis Maior es una de las constelaciones más fáciles de localizar debido a que contiene a la estrella más brillante del cielo nocturno.
- La estrella más brillante de Canis Maior es Sirio, la cual tiene una magnitud aparente de −1,46.
- El cuerpo de cielo profundo más notable de Canis Maior es el cumulo estelar M41 (NGC 2287).






