Aquarius Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Aquarius (The water bearer)
Aquarius is one of the 12 constellations of the zodiac family. In Latin, the constellation Aquarius means "the bearer of water," and the history of this constellation comes from Greek mythology.
The location of the constellation Aquarius is in the southern hemisphere. However, it is also visible in the northern hemisphere of the Earth.
We can find it in the night sky throughout the fall in the northern hemisphere and spring in the southern hemisphere.
The constellation Aquarius is the home of deep-sky objects such as galaxies. In addition, within the constellation's boundaries, there are occurrences of several meteor showers.

The Mythology And History Of The Aquarius Constellation
Ancient Egypt


In ancient Egyptian mythology, the constellation Aquarius was associated with the Nile river god "Hapi," who held an urn with water.
The myth tells that the floods of the Nile occurred when the god Hapi turned his jug of water upside down, overflowing the river.
Greek Mythology


TIn Greek mythology, Aquarius holds a water pitcher that spills out and relates the constellation to the flood that wiped out all humanity except Deucalion and his wife, Pyrrha.
The character representing the constellation Aquarius is usually Ganymede from Greek mythology.
Ganymede was a handsome young Trojan who caught the attention of Zeus, who disguised himself as an eagle to take him to Olympus and serve as an assistant to the gods.
Early Modern Period


As well as other constellations seen more prominently in the south, the constellation Aquarius belongs to the group of constellations associated with water.
During the time of exploration, which spans from the early fifteenth century to the late seventeenth century, sailors used this group of constellations to guide themselves on their way.
Nowadays


Today Aquarius remains one of the 12 constellations of the zodiac and is recognized by theInternational Astronomical Union.
Its borders have undergone little or no modification since its designation. It is very tenuous and has almost no very bright stars.
It is an essential study body in astronomical research since it has critical planetary nebulae and extrasolar planets.
Note: An extrasolar planet is any planet that orbits a star other than the Sun. They are also known as exoplanets.
How To Find The Cancer Constellation?
Visibility By Region
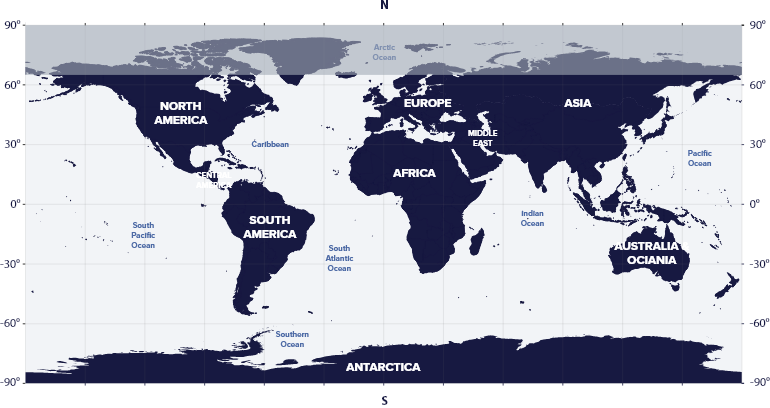

Aquarius resides in the fourth quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (SQ4) at latitudes between 86° S and 65° N, which means we can see the constellation in the night sky from almost all parts of the world, including the areas of Antarctica closest to the Tropic of Capricorn.
Aquarius is visible from North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica.
Visibility By Season
Aquarius is a seasonal constellation, which means it can't be seen in the sky all year round. It belongs to the group of northern autumn constellations.
The Sun crosses the region of the constellation Aquarius every year from January 20 to February 18. Therefore, it is not visible on those dates. The best month to observe this constellation is in October.
Finding Aquarius Constellation
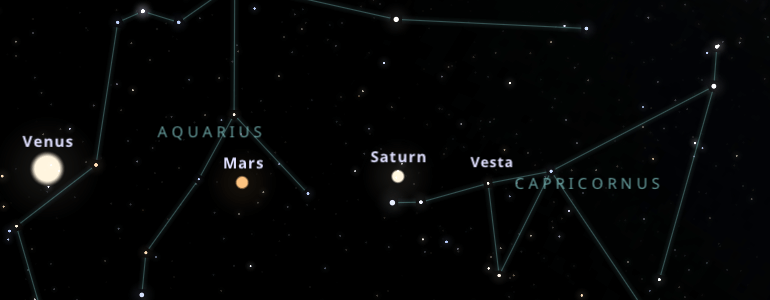

Aquarius is a very faint constellation and has almost no very luminous stars.
The best way to locate it is with one of its neighbors, in this case, Capricorn.
Like all constellations of the zodiac, Capricorn and Aquarius are located on the elliptical. This imaginary line traces the Sun in the sky for over a year.
Capricorn is easy to locate as it has brighter stars and arrow shapes pointing downwards.
If you look at it from the northern hemisphere, the arrow points down, but from the southern hemisphere, the arrow points up.
Once we have located Capricorn, we have to follow the line towards the constellation of Pisces, and we will come across the constellation of Aquarius.
Aquarius is between the constellations of Capricorn and Pisces.
Related Constellations
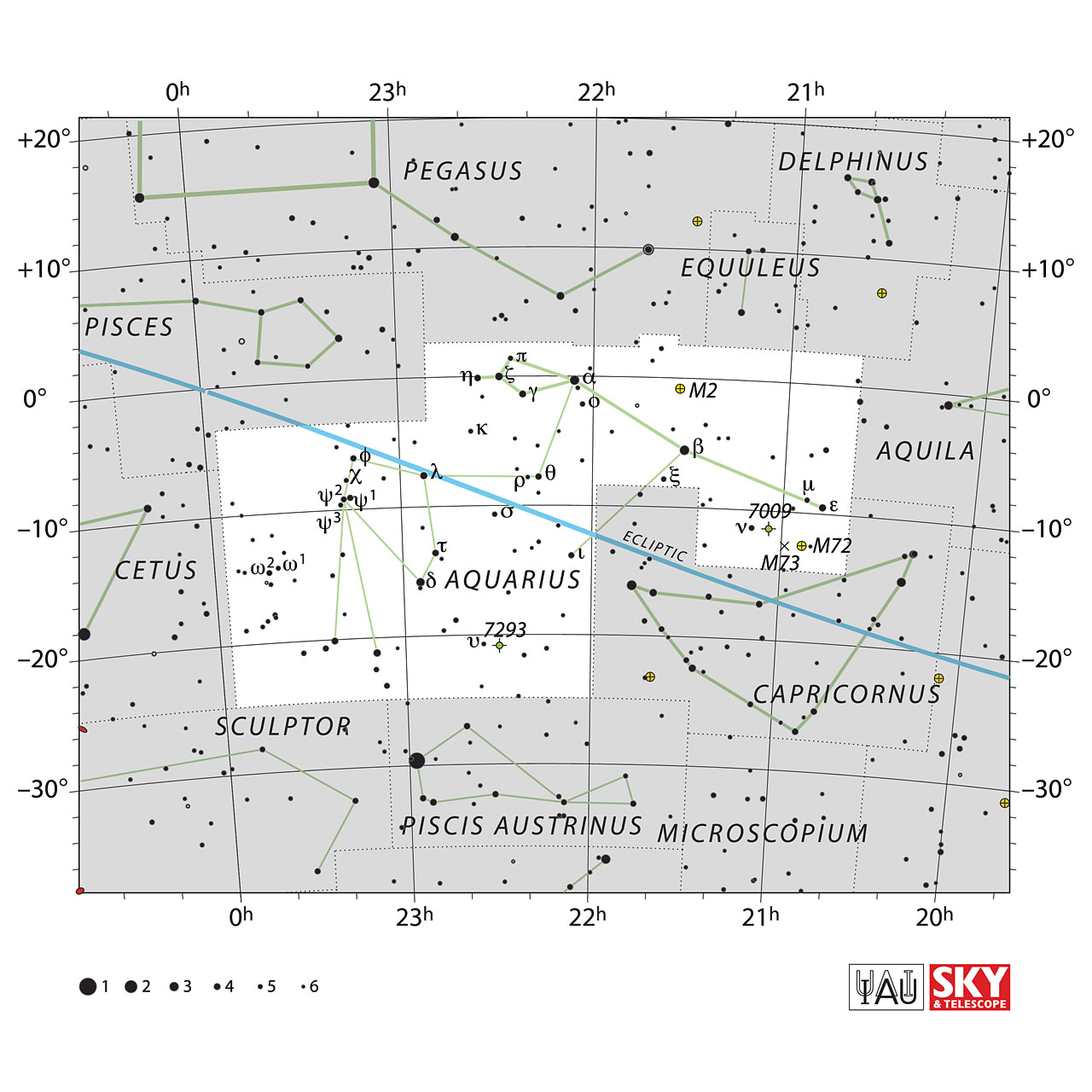

The bordering constellations of Aquarius are Aquila, Capricornus, Cetus, Delphinus, Equuleus, Pegasus, Pisces, Piscis Austrinus, and Sculptor.
Aquarius belongs to a group of 12 zodiacal constellations along with Gemini, Taurus, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpius, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aries, and Pisces.
Stars in Aquarius Constellation
The brightest stars in Aquarius are Sadalsuud (β Aquarii), Sadalmelik (α Aquarii)and Skat - δ Aquarii (Delta Aquarii).
In addition, it has some stars with proper names designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These stars are Albali, Ancha, Bosona, Bunda, Lionrock, Márohu, Sadachbia, Sadalmelik, Sadalsuud, Situla, and Skat.
Officially Aquarius has 172 stars within its borders, of which 22 are the main stars that shape the constellation.
There are also several binary stars within this constellation: the 2-star systems. In addition, Aquarius has variable stars that change their magnitude (brightness) during the year and star clusters.
Sadalsuud - β Aquarii (Beta Aquarii)
Sadalsuud is the most luminous star in the constellation Aquarius; it is approximately 540 light-years away.
It is a yellow supergiant with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.87, a mass six times that of the Sun, and 2,200 times more luminous.
It is of multiple stars whose main component is Beta Aquarii A.
Sadalmelik - α Aquarii (Alpha Aquarii)
Located about760 light-years away from the Solar System, Sadalmelik is the second brightest Aquarius.
Like β Aquarii, it is a yellow supergiant star of spectral type G2Ib, of apparent magnitude +2.95.
Sadalmelik, Sadalsuud, and Enif (ε Pegasi) likely have a common origin that relates them as they share many characteristics such as similar age and mass.
Gliese 876
With only 32% of the mass of our local star (the Sun), Gliese 876 is a relatively small star. The temperature on its surface is lower than the Sun, and a radius is also smaller.
It is only 15 light-years from our solar system, so it is one of the closest stars. According to chromospheric activity, the star is between 6520 and 9900 million years old.
As of 2007, at least four extrasolar planets orbiting the star have been confirmed, Gliese 876 b, Gliese 876 c, Gliese 876 d, and Gliese 876 e.
The four planets are of the Jupiter type, and although they are very close to their star, how it is smaller than the Sun, they are all within the habitable zone.
As these are gaseous planets, it is unlikely that they have life. That is why astronomers are studying this star system in search of "exomoons" that orbit the exoplanets, since they could host liquid water and, therefore, also life.
Other Aquarius Stars:
- Aquarii δ (Skat)
- Aquarii ε (Albali)
- Aquarii ζ
- θ Aquarii (Wide)
- λ Aquarii (Hydor)
- and Aquarii
- ο Aquarii
- π Aquarii (Seat)
- υ Aquarii
- Aquarii φ
- χ Aquarii
- Aquarii ψ
- ψ1 Aquarii
- ψ2 Aquarii
- ω1 Aquarii
- ω2 Aquarii
- 1 Aquarii
- 11 Aquarii
- 25 Aquarii (d Aquarii)
- 53 Aquarii
- 88 Aquarii (c2 Aquarii)
- 94 Aquarii
- R Aquarii
- AE Aquarii
- IN Aquarii (3 Aquarii)
- ET Aquarii (108 Aquarii)
- EZ Aquarii
- FK Aquarii (Gliese 867)
- HD 210277
- Gliese 849
- Wolf 940
- Gliese 884
- GJ 1276 (WD 2251-070)
- BD-22 5866 (LP 875-68)
- TRAPPIST-1
Deep Sky Objects


Aquarius is also known as the home of several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies), or galaxies.
In the case of Aquarius, it is rich in several notable galaxies, star clusters, and planetary nebulae; some of them are:
Nebulosa Helix, NGC 7293
Also known as the "Eye of God" nebula, this is one of the most famous planetary nebulae due to its shape and color.
It is in the constellation Aquarius 680 light-years from our solar system.
X-ray observations have revealed that this nebula consists of two perpendicular gas disks, the most recent being 6600 years old, and the oldest one emerged 12,000 years ago.
Messier 2 (M2, NGC 7089)
M2 is a globular cluster 13 billion years old, containing about 150,000 stars, including 21 variables used to calibrate interstellar distances.
Because it has a diameter of 175 light-years, it is one of the most accessible globular clusters to find and one of the most famous.
It is 37.500 light-years from the Sun and has an apparent magnitude of 6.3.
Saturn Nebula (NGC 7009, Caldwell 55)
Its appearance closely resembles Saturn, located approximately 3,000 light-years from Earth, and has an apparent magnitude of 12.8.
The Saturn Nebula is a planetary nebula with a white dwarf at its center that is not visible to the naked eye. The central star has a brightness equivalent to 20 suns, and its temperature is about 55,000 K.
Other objects of deep space of Aquarius:
- Globular cluster M2
- M72
- M73
- Globular cluster NGC 7492
- Spiral galaxy NGC 7727.
- Aquarius Dwarf Galaxy
Meteor Showers


Within the constellation's boundaries of Aquarius occurs one of the best star showers of the year called the "Eta Aquariid", rain is visible from April 21 to May 20 each year, and peak activity occurs on May 6.
This shower meteor originates from the remnants of ice, dust, and rocks left by the famous Halley's Comet.
Interesting Facts
- The symbol of the constellation Aquarius represents the flow of water.
- Although the "Eta Aquariid" is Aquarius' most famous meteor shower, four other meteor showers occur within its boundaries.
- Aquarius is part of a group of constellations that are associated with water. Within this group are Pisces (the fish), Eridanus (the river), Cetus (the whale), Capricornus (the sea-goat), Delphinus (the dolphin), and Hydra (the water snake).
Conclusions
- Since Aquarius is a zodiac constellation, it belongs to the zodiac family's constellations.
- Aquarius means "the bearer of water," derived from Greek mythology, where the character representing the constellation of Aquarius is Ganymede.
- Aquarius is a southern constellation, but we can see it from all the northern hemisphere countries. The best time to observe Aquarius is October.
- Aquarius is difficult to locate because the main stars are not bright enough. The best way to find it is by first locating the constellation of Capricorn and following the Ecliptic towards Pisces.
- The brightest stars in Aquarius are Sadalsuud (β Aquarii), Sadalmelik (α Aquarii) and Skat - δ Aquarii (Delta Aquarii).
- The most notable deep sky body of Aquarius is the constellation of the Helix due to its shape and colors, and it is also known as the Eye of God Nebula.
- The strongest meteor shower in Aquarius is the "Eta Aquariid".







