Cygnus Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Cygnus (The swan)
Cygnus is one of the most prominent constellations in Earth's northern hemisphere.
The constellation's name comes from Latin and means "Swan," in Greek mythology, it is associated with the swan into which Zeus transformed to seduce Leda, daughter of the king of Aetolia.
Cygnus is one of the constellations most accessible to see in the sky due to its brightness and proximity to the north pole.
The fastest way to locate it is because it forms an asterism of populous stars known as"The Northern Cross."
The brightest star in Cygnus is Deneb, which has a magnitude of 1.34 and is part of the asterism of stars called "The Summer Triangle."
Cygnus is also home to deep-sky objects such as galaxies, star clusters, and star nebulae.
In addition, within the constellation's boundaries, there are occurrences of several significant meteor showers.

The Mythology And History Of The Cygnus Constellation
Ancient Egypt


The ancient Egyptians had the belief that the constellation of Cygnus was marked as a portal to the celestial world.
According to historian Andrew Collins, it is possible that the three pyramids of Giza were aligned with this constellation.
In addition, in the Zodiac of Dendera, there is a northern constellation in which a cross can be observed; archaeologists maintain that it is the asterism that we currently call "The northern cross."
Although Cygnus was not mentioned in hieroglyphs, it is most likely that the Egyptians recognized it by another name and associated it with another creature, such as the silhouette of a crocodile.
Greek Mythology


In ancient Greece, there was the myth in which Zeus disguised himself as a swan to seduce Leda.
But the story that is most associated with the constellation Cygnus is that of two friends named Phaeton and Cygnus. Phaeton was the mortal son of the sun god Helios and Cycnus was Phaeton's best friend.
One day both friends rode their carriages too close to the sun. They ended up on fire, rushing to the Earth, where Cycnus survives. Still, Phaeton's body remains at the bottom of the Heridanis River.
Then Cycnus makes a deal with Zeus to turn him into a Swan. With his new animal form, he manages to get the lifeless body of his friend Phaetonout of the river to give him a dignified burial and his soul peace.
Zeus is moved by the action of Cycnus and immortalizes him by turning him into the swan-shaped constellation.
Early Modern Period


At the time of navigation, during the tenth and sixteenth centuries, travelers began to use the constellation Cygnus as a reference to mark the regions near the north.
The prominent star asterism of the constellations is named "The Northern Cross". It is mentioned in several papyri and books of travelers crossing the Sahara Desert.
Later in modern astronomy, Cygnus would be related to other constellations forming the asterism of stars called"The Summer Triangle."
Nowadays


Currently, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) is in charge of defining the boundaries of the constellations, and Cygnus remains unchanged in its territorial limits.
Cygnus covers a total area of 804 square degrees, being one of the 16largest buildings of all.
In the field of research, Cygnus contains significant deep-sky bodies for the study of star formation, such as planetary nebulae.
How To Find The Cygnus Constellation?
Visibility By Region
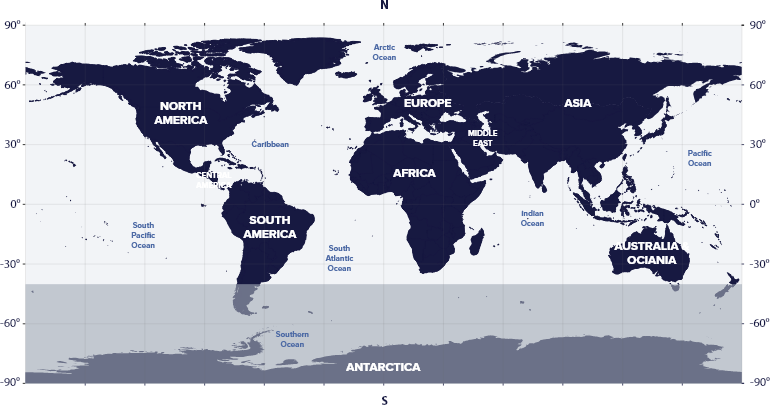

The constellation of Cygnus resides in the fourth quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ4), at latitudes between 40° S and 90° N.
We can see the Cygnus constellation in the night sky in all northern hemisphere countries, such as the USA, Russia, the entire European continent, China, India, Egypt, and Japan.
Cygnus is not visible in regions below the Tropic of Capricorn, such as Buenos Aires, Argentina, Uruguay, South Africa, South Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica.
Visibility By Season
Cygnus is visible between mid-June and early October in both hemispheres, classified as an autumn constellation in the northern hemisphere and spring in the southern hemisphere.
The best month to see the constellation Cygnus is in September.
Finding Taurus Constellation
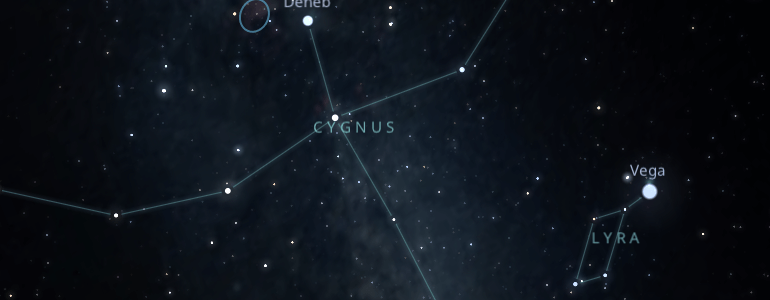

One of the easiest methods is locating "The Northern Cross," an asterism of 5 stars that form a cross right in the middle of Cygnus's constellation.
Another method that can be useful is to navigate from the star Vega of the constellation of Lyra and draw a straight line you would imagine towards the constellation of Pegasus; right in the middle of the two, you will find the northern cross, and you will be able to see the entire constellation of Cygnus.
Related Constellations
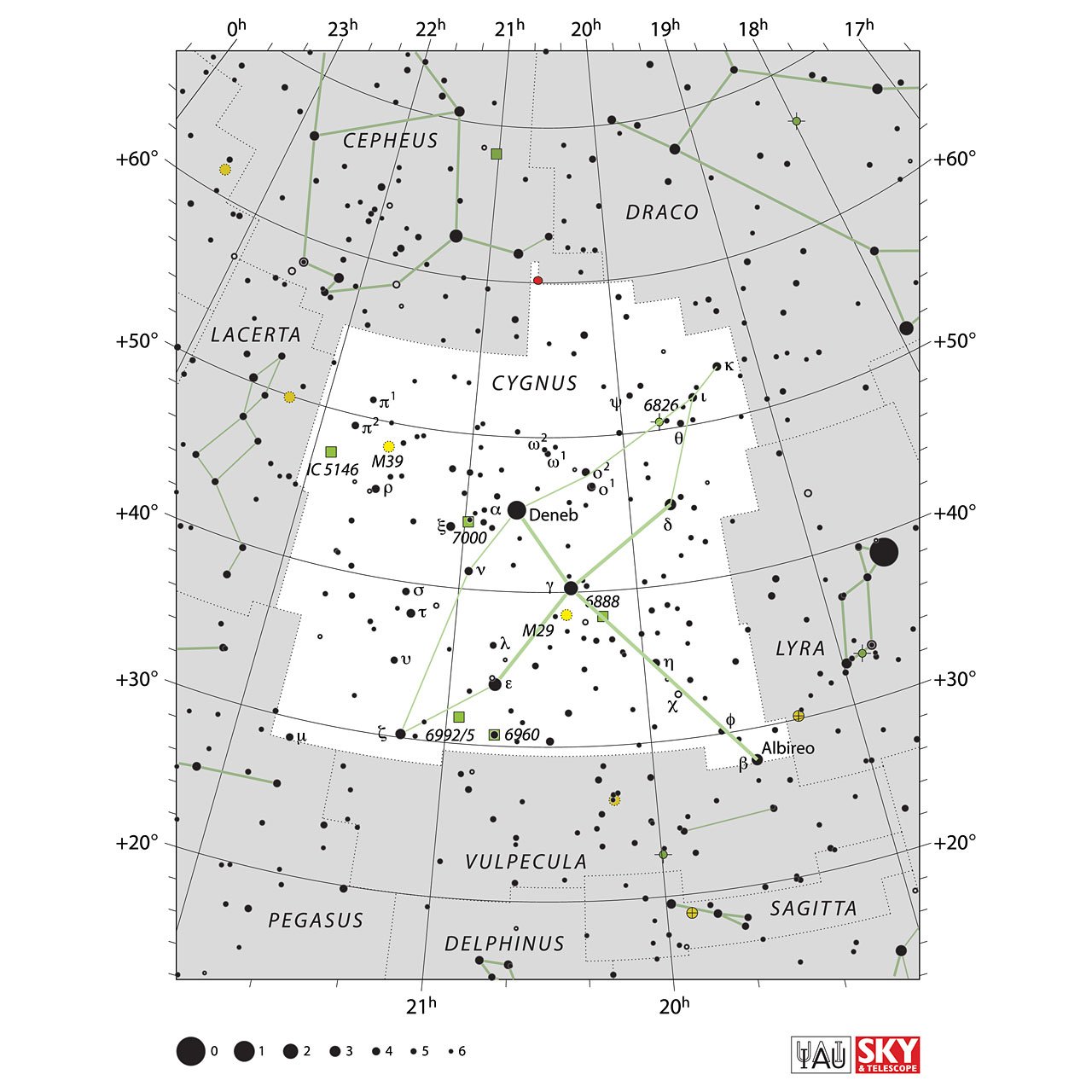

Stars in Cygnus Constellation
Cygnus officially has 262 stars, of which six have proper names designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU); these stars are Albireo, Aljanah, Azelfafage, Deneb, Fawaris, and Sadr.
Deneb (α Cygni)
It is the brightest star in the constellation Cygnus; it is a white supergiant of spectral type A2Iae, with an apparent magnitude of 1.35.
It is located 1425 light-years from Earth, and the most up-to-date calculations estimate that it is 54,400 more luminous than the sun being 250 times larger than our sun.
Cygni γ (γ Cyg / 37 Cygni)
Located 1520 light-years from Earth, Cygni is the second brightest star in the constellation at a magnitude of 2.23.
(ε Cygni / 53 Cygni)
Also known by giennah, it is the third brightest star in the constellation Cygnus. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.48 and lies at 72 light-years from the solar system.
Other Cygnus Stars:
- β Cygni (Albireo)
- δ Cygni (Fawaris)
- ε Cygni (Aljanah or Giennah)
- ζ Cygni
- η Cygni
- λ Cygni
- ξ Cygni
- ο Cygni
- ρ Cygni
- σ Cygni
- τ Cygni
- χ Cygni
- ω1 Cygni
- ω² Cygni (Ruchba)
- 11 Cygni
- 16 Cygni
- 17 Cygni
- 29 Cygni
- 41 Cygni
- 52 Cygni
- 59 Cygni (V832 Cygni)
- 61 Cygni
- P Cygni
- X Cygni
- RV Cygni
- RW Cygni
- BC Cygni
- TT Cygni
- KY Cygni
- V444 Cygni
- NML Cygni (V1489 Cygni)
- V1687 Cygni
- HD 184499
- HD 188753
- A11 and A36
- WR 142
- BD+40 4210
- Gliese 777
- GJ 1245 (V1581 Cygni)
- Cygnus X-1
- BD+43 3654
Deep Sky Objects


Cygnus is also home to various deep sky objects. Deep-sky objects are celestial bodies different from stars, such as nebulae (interstellar cloud bodies) or galaxies.
Cygnus has many deep-sky bodies, such as galaxies, nebulas, and star clusters; these are:
- M29, open group.
- M39, open cluster.
- NGC 7000, North America Nebula.
- IC 5070 Pelican Nebula.
- Nebula NGC 6960, supernova remnant.
- NGC 6888, Crescent Nebula
- NGC 6826 (Blinking Eye Nebula),
- NGC 6884,nebula.
- NGC 7027. nebula.
- Egg Nebula (RAFGL 2688), bipolar planetary protonebula.
- HB 21, supernova remnant.
- SNR G067.7+01.8, a supernova remnant.
- CTB 80, supernova remnant.
- CTB 87, supernova remnant.
- W63, supernova remnant.
- NGC 6946, Galaxy.
- Cygnus X, star-forming region.
Meteor Showers


In the region comprising the constellation Cygnus occurs a meteor shower called "Kappa Cygnids."
This occurs between August 3 and August 25, with the peak of maximum observation on August 17.
Interesting Facts
- There is a Mexican science fiction film called Cygnus. The plot revolves around a signal of extraterrestrial origin from the constellation Cygnus.
- The famous star asterism called "The Summer Triangle" is formed by the star Deneb of the constellation Cygnus, the star Vega of the constellation of Lyra, and the star Altair of the constellation Aquila.
- Cygnus is part of an ancient story related to 3 birds called "Birds of The Stymphalus," so it is directly related to the constellation Aquila, Lyra, and Sagittarius.
Conclusions
- Cygnus is a northern circumpolar constellation whose name comes from the Latin meaning "Swan" and is also known as "The Northern Cross."
- Cygnus is a northern constellation, but it is possible to see it in some countries of the southern hemisphere that are above the Tropic of Capricorn.
- It is impossible to see Cygnus from regions far south such as New Zealand, Argentina, or Antarctica.
- Cygnus is one of the easiest constellations to locate because it is part of the summer triangle, a famous asterism in the northern hemisphere formed by Altair, Deneb, and Vega.
- The brightest star in Cygnus is Deneb, with an apparent magnitude of 1.35, being the fifth brightest star in the night sky.
- The most noticeable galaxy within the borders of Cygnus is NGC 6946.
- The strongest meteor shower in Cygnus is the "Kappa Cygnids," which occur in August each year.







