Monoceros Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Monoceros (The unicorn)
Monoceros is a constellation located at the Earth's celestial equator. The name of the constellation comes from Greek and means Unicorn.
The location of the constellation Monoceros is right at the celestial equator; that is, it is possible to see it in both hemispheres of the Earth.
Monoceros is a medium-sized constellation and does not have high-magnitude stars, meaning it is very faint to look at.
The brightest star of Monoceros is Beta Monocerotis (Cerastes / β Mon) with a magnitude between +3.76.
Despite being a relatively new constellation, Monoceros contains many deep-space bodies such as the Galaxies and Nebulae.
In addition, within the constellation's boundaries, a meteor shower occurs.

The Mythology And History Of The Monoceros Constellation
Ancient China


Monoceros is one of the most recent constellations to be added to the complete list of sky constellations. It is very faint, and hardly other cultures could see it with the naked eye throughout history.
In ancient Chinese culture, astronomers cataloged a series of Asterisms known as Sze Fūh, in English "Four Great Canals."
Also mentioned are the asterisms Kwan Kew; and Wae Choo, which means "the outdoor kitchen."
These asterisms lie within the boundaries that currently correspond to the constellation Monoceros. The Chinese were the first to recognize this region as an actual constellation.
Early Modern Period


The constellation Monoceros first appeared on a celestial globe created by Dutch cartographer Petrus Plancius in 1612.
Later the German astronomer Jakob Bartsch would associate it with the shape of a Unicorn in his star chart in 1624.
Monoceros means Unicorn in Greek.
Nowadays


Since its introduction into celestial maps as one more constellation of the sky and not as part of other constellations, Monoceros has not undergone significant changes in its boundaries.
In scientific research, Monoceros is an essential region for studying the evolution of stars since, within its areas, there are various deep space bodies as planetary nebulae.
How To Find The Monoceros Constellation?
Visibility By Region
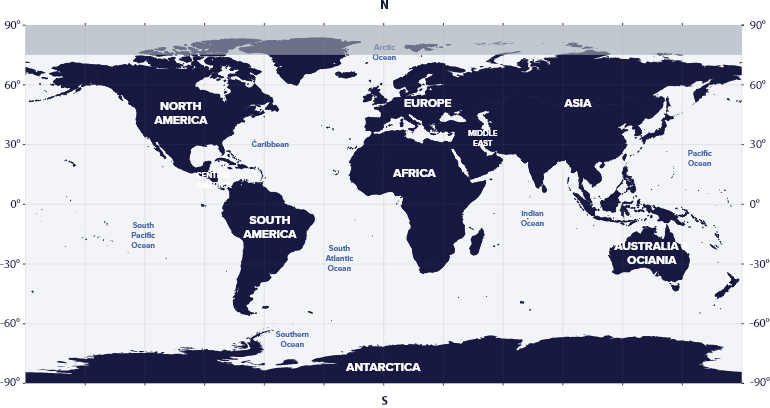

The constellation Monoceros resides in the second quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere (NQ2), at latitudes between 75° S and 90° N, which means we can see the constellation in the night sky in every country in the world, including Antarctica.
Monoceros is visible in the USA, Europe, Russia, China, or Japan in the northern hemisphere.
However, it is not visible in regions far north, such as northern Canada, northern Norway, or northern Russia.
Monoceros is visible in all the southern hemisphere countries and a small Antarctica region.
Visibility By Season
Monoceros is an equatorial constellation visible both in the northern and Earth's southern hemispheres.
Being at the Equator, Monoceros is visible all year round, but the best month to see the Monoceros constellation is February.
Finding Monoceros Constellation
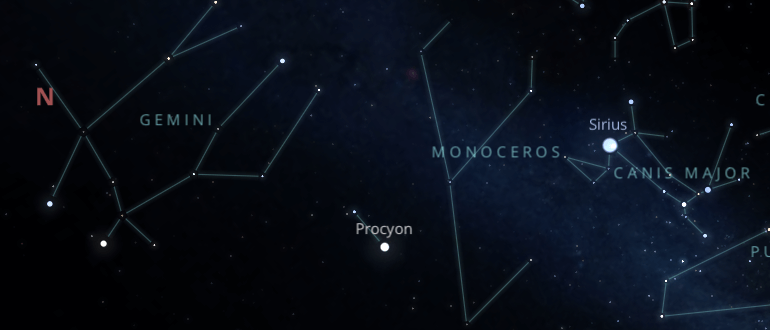

Monoceros is on the celestial equator, so in the northern hemisphere, you must look South. In contrast, if you are in the south, you must look slightly towards the north, and if you are at the equator, you must look at the zenith.
Monoceros is a medium constellation but very faint; it is complicated to see in the sky with light pollution.
The best way to locate it is by drawing an imaginary straight line from the star Sirius of Canis Major's constellation to Gemini's constellation. Monoceros is located right in the middle of those two constellations.
Related Constellations
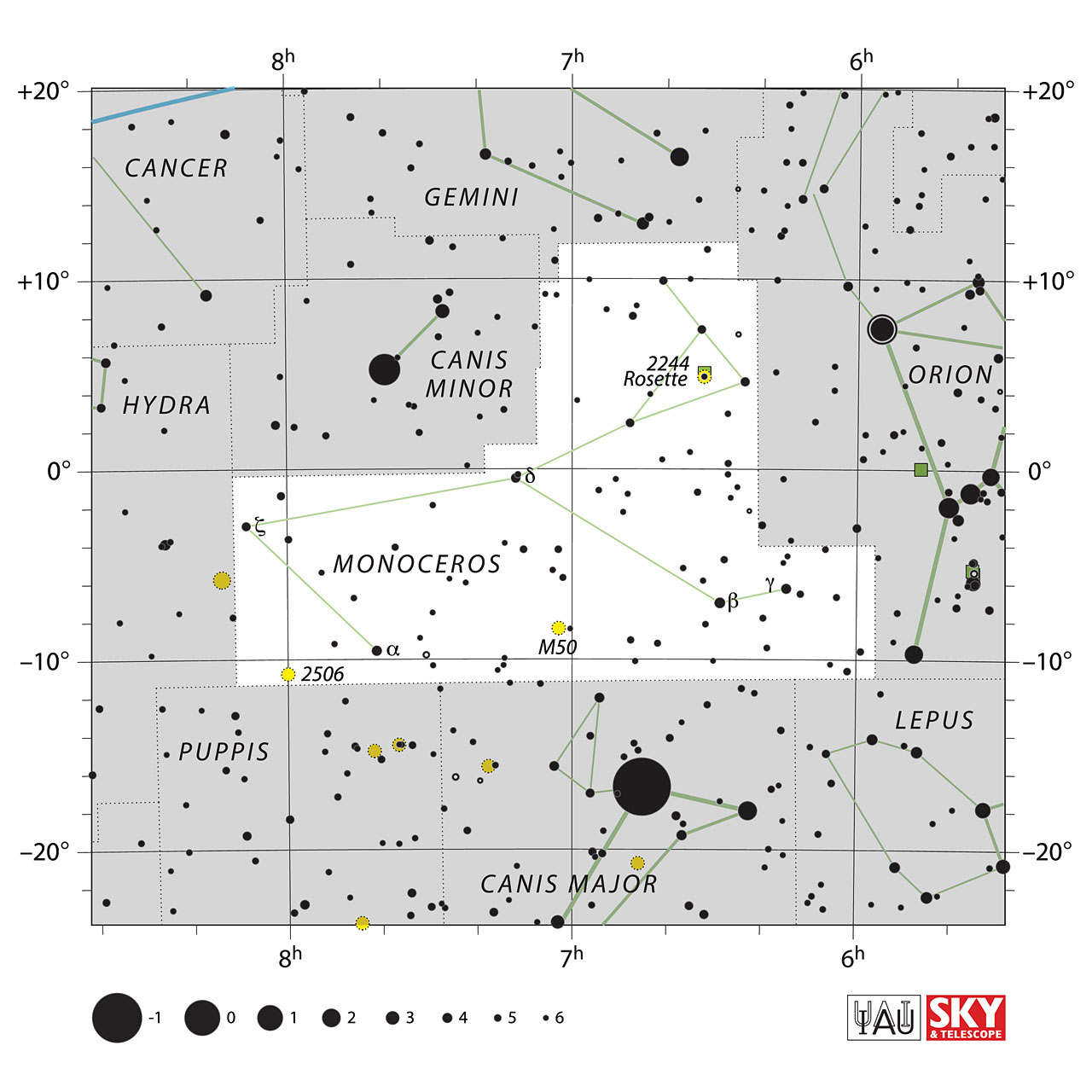

Monoceros' related constellations are Canis Major, Canis Minor, Gemini, Hydra, Lepus, Orion, and Puppis.
Monoceros belongs to the Orion family of constellations; these include Canis Major, Canis Minor, Lepus, and Orion.
Stars in Monoceros Constellation
Monoceros officially has 138 officially recognized stars, of which 5 form the central figure of the constellation; these are Alpha Monocerotis, Gamma Monocerotis, Delta, Monocerotis, Zeta Monocerotis, and Beta Monocerotis.
Beta Monocerotis (Cerastes / β Mon)
With an apparent magnitude of 3,76, Cerastes is the brightest star in the constellation Monoceros; it is a triple star system located at 690 light-years from the Solar System.
Alpha Monocerotis (α Mon / Lucida / Ctesias / 26 Monocerotis)
Located at 144 light-years from Earth, Lucida is the second brightest star in the constellation Monoceros with an apparent magnitude of 3.94.
Gamma Monocerotis (Tempestris / γ Monocerotis)
Tempestris is the third brightest star in the constellation Monoceros with an apparent magnitude of 3.9, located at 645 light-years from Earth.
Other Monoceros Stars:
- δ Monocerotis(Kardan), a white star of magnitude 4.15.
- ε Monocerotis, estrella binary.
- ζ Monocerotis, a yellow supergiant of magnitude 4.37.
- 3 Monocerotis, binary star.
- 13 Monocerotis, white supergiant 10,800 times more luminous than the Sun.
- 19 Monocerotis, Beta Cephei variable of magnitude 4.99.
- 20 Monocerotis, giant orange of magnitude 4,92.
- 25 Monocerotis, white-yellow giant of magnitude 5.14.
- 27 Monocerotis, orange giant of magnitude 4.94.
- 28 Monocerotis (V645 Monocerotis), orange giant of magnitude 4.69.
- R Monocerotis, variable star.
- S Monocerotis (15 Monocerotis), blue giant.
- T Monocerotis, Cepheid variable.
- U Monocerotis, variable RV Tauri.
- W Monocerotis, irregular variable.
- RV Monocerotis, semi-irregular variable.
- DD Monocerotis: It's eclipsing binary star.
- V700 Monocerotis (MWC 147), Herbig star type Ae/ Be.
- V715 Monocerotis, blue giant of magnitude 6.15.
- V789 Monocerotis, binary star.
- V838 Monocerotis
- Plaskett's Star (HR 2422): Is a binary system.
- HD 45652: A star of magnitude 8.13 with a planetary system.
- HD 46375: Is an orange subgiant with an extrasolar planet of the "hot Jupiter" type.
- HD 50064, blue hypergiant star.
- HD 52265: Is a yellow dwarf with a gas giant planet.
- Ross 614 (V577 Monocerotis), red dwarf.
- Gliese 250, binary star 28.4 light-years away.
Deep Sky Objects
Monoceros is a little-studied constellation; most of its deep sky objects are still in the study phase.
The only two deep-sky bodies in Monoceros that the International Astronomical Union officially recognizes are:
- M50, an open star cluster
- The Rosette Nebula (NGC 2237): Is a diffuse nebula with an overall magnitude of 6.0 to 4900 light-years from Earth.
- (NGC 2264) The Christmas Tree Group: Is another open group of fairly bright stellar nebulae with an overall magnitude of 3.9 to 2400 light-years from Earth.
- (NGC 2264) The Cone Nebula is a very faint nebula containing a darkened cone-shaped structure.
- NGC 2254: An open cluster with a total magnitude of 9.7 located 7100 light-years from Earth.
- (NGC 2261) The Hubble Variable Nebula: Is a nebula with an approximate magnitude of 10 located 2500 light-years from Earth.
- IC 447: A reflection nebula.
Meteor Showers


The constellation Monoceros is associated with the most minuscule seven meteor showers. Still, the brightest of all is known as Alpha Monocerotids.
The Alpha Mon Ocerotids meteor shower occurs between November 15-25, and the peak of maximum observation occurs on November 21.
Conclusions
Monoceros is a constellation located on the celestial equator; the German astronomer Jakob Bartsch was the first to assign it a name who associated it with the shape of a Unicorn in his star chart in 1624.
Because it is on the celestial equator, Monoceros is visible in all world countries all year round, including Antarctica.
The best month to see the constellation Monoceros is in February.
The brightest star of Monoceros is Beta Monocerotis (Cerastes/β Mon)with an apparent magnitude of 3.76.
The best way to locate the constellation Monoceros is to draw an imaginary straight line from the star Sirius of the constellation Canis Major to the constellation Gemini. Monoceros is located right in the middle of those two constellations.
Monoceros' most notable deep-sky body is the star cluster M50.
The strongest meteor shower in Monoceros is Alpha Monocerotids.






