Reticulum Constellation: The Ultimate Guide
Reticulum (The net)
Reticulum is one of the constellations located in the southern celestial hemisphere. The name of the constellation comes from Latin and means "Recticula."
A reticle is a tool placed on the outside of a telescope lens to measure the position of stars.
The location of the constellation Reticulum is essentially in the southern hemisphere and is fully visible from latitudes below 23° north.
Reticulum occupies an area of only 114 square degrees. This makes it the seventh smallest constellation in the entire night sky.
The brightest star in the constellation Reticulum is Alpha Reticuli (α Ret / HD 27256 / HR 1336), with an apparent magnitude of +3.34.
The constellation Reticulum is also home to deep-cooling objects, mainly galaxies.
There is no occurrence of meteor showers within the boundaries of the constellation.

The Mythology And History Of The Reticulum Constellation
Reticulum is classified as one of the 88 modern constellations, meaning that it has no associated history in ancient Western cultures because it was not visible in those regions.
It is known that Reticulum is one of the faintest constellations and that most of its stars cannot be seen with the naked eye, so it was necessary to wait for telescopes to be invented to see it.
Early Modern Period


This constellation was introduced by the professor of astronomy and mathematics, Isaac Habrecht II, on his celestial globe in 1621, giving it the name of Rhombus.
In 1756 the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille; during his stay at the Cape of Good Hope, he renames the constellation le Réticule Rhomboide to commemorate the lattice of his telescope's eyepiece.
Later that name was Latinized to Reticulum in his stellar catalog Coelum Australe Stelliferum.
Nowadays


In 1922 the International Astronomical Association added the constellation Reticulum to the 88 official night sky constellations as an independent constellation. Since then, it has not undergone significant modifications in its limits or name.
Reticulum currently covers a total area of 114 square degrees. This makes it the seventh smallest constellation in the entire night sky.
How To Find The Reticulum Constellation?
Visibility By Region
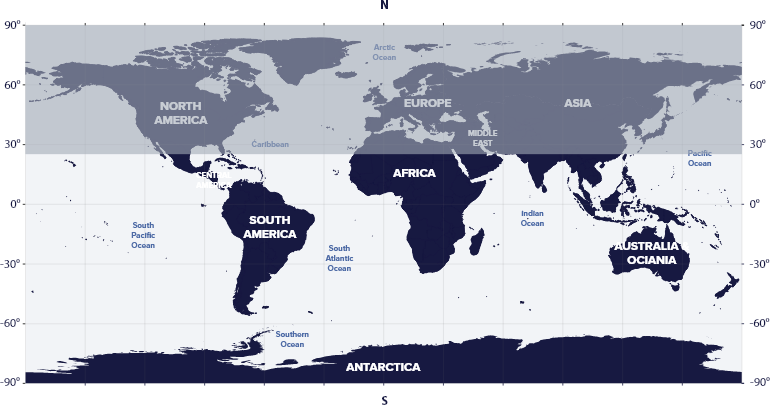

Reticulum resides in the first quadrant of the Southern Hemisphere (SQ1) between latitudes 23° N and 90° S, which means that we can see the constellation in the night sky from all countries of the southern hemisphere of the earth and some countries of the northern hemisphere.
The constellation Reticulum is visible in the Americas, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica.
Reticulum is not visible in regions above 23°N such as Canada, most of Europe such as Italy, France, or Germany, nor in Russia, Greenland, Japan, and Alaska.
Visibility By Season
The best month to visualize the Golden constellation is in January, which means that it is visible during the winter in the northern hemisphere. While in the southern hemisphere it is visible during the summer.
Finding Reticulum Constellation
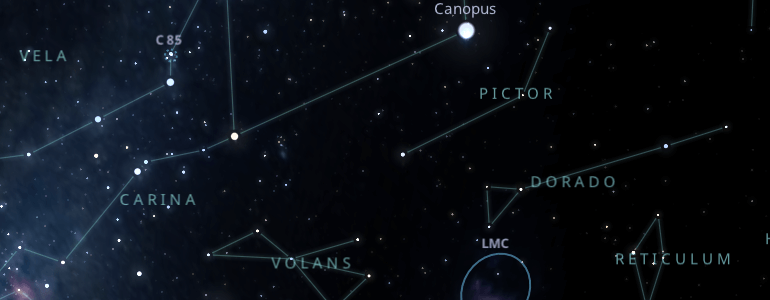

The constellation Reticulum has no stars of the first or second magnitude; it is very faint. However, it is very close to Canopus's star, the second brightest in the sky.
The easiest way to locate the constellation Reticulum is to locate the star Canopus in the constellation Carina. Then we draw an imaginary straight line from Canopus to the star Achernar. The constellation Reticulum is located halfway between the two stars.
Related Constellations
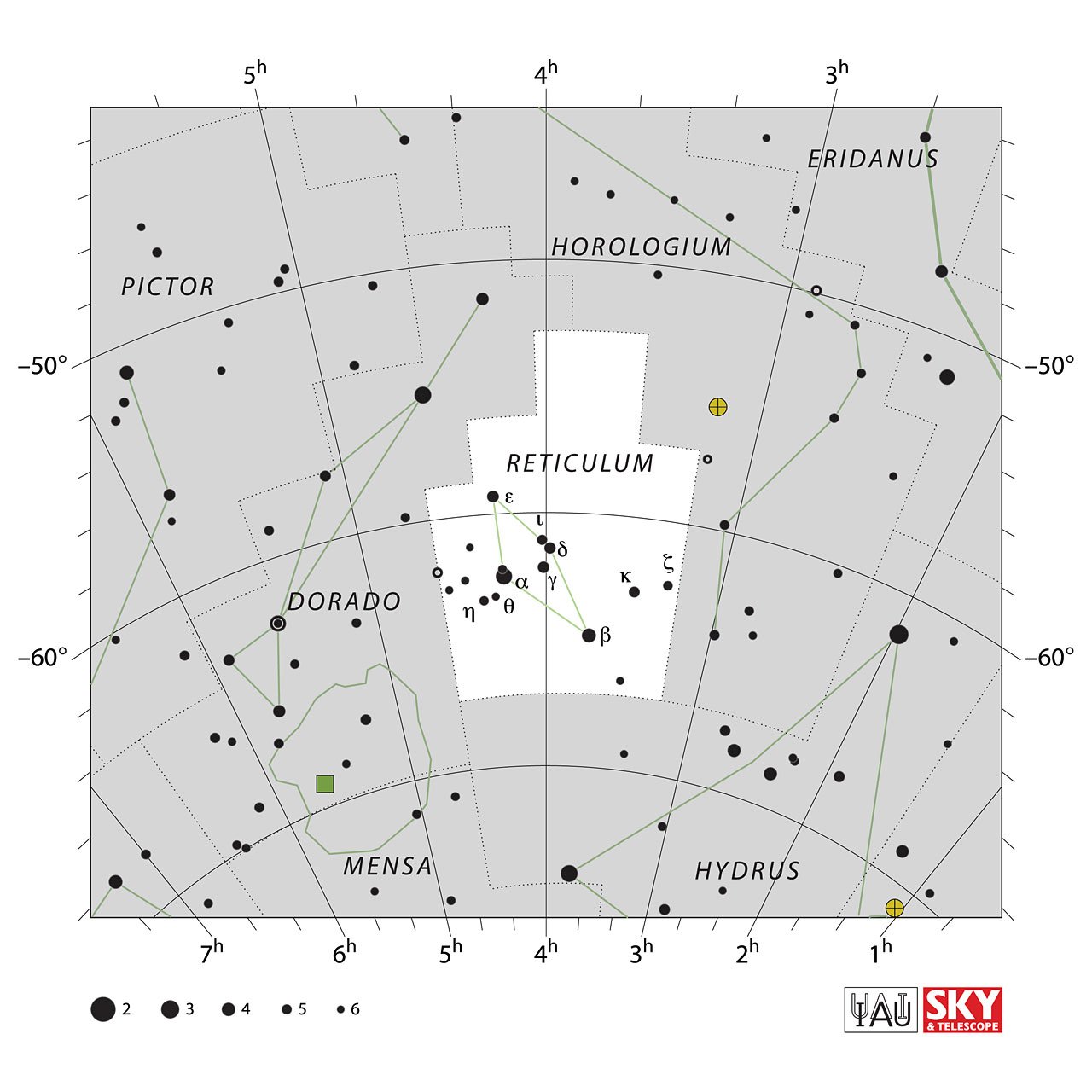

The constellations bordering Reticulum are Horologium, Dorado, and Hydrus.
In addition, Reticulum belongs to the family of the constellations of Lacaille; these include Antlia, Caelum, Circinus, Fornax, Horologium, Mensa, Microscopium, Norma, Octans, Pictor, Sculptor, and Telescopium.
Stars in Reticulum Constellation
The constellation Reticulum officially contains 23 stars, of which 7 form the central figure of the constellation; these are Alpha Reticuli, Beta Reticuli, Epsilon Reticuli, Gamma Reticuli, Delta Reticuli, Kappa Reticuli, and Iota Reticuli.
Alfa Reticuli (α Ret / HD 27256 / HR 1336)
It is the brightest in the constellation Of Reticulum, with a star of an apparent magnitude of +3.34. This is only visible south of the Tropic of Cancer; it has no traditional name. It is located 163 light-years away from the Solar System.
Alpha Reticuli is a luminous yellow giant of spectral type G8II-III with a surface temperature of 4940 K. 237 times more luminous than the Sun. He has a radius 21 times larger than the solar radius.
Beta Reticuli ( Beta Ret , β Reticuli , β Ret )
It is a binary stellar system in the constellation Reticulum. With an apparent visual magnitude of +3.84, it is the second brightest star in the constellation. This is about 97 light-years from the Sun.
The principal, main component "A" is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K0 IVSB, between 5 and 6 billion years old and 1.2 times the mass of the Sun.
The secondary component "B" is probably a red dwarf with a classification in the range M0-M4.
Other Reticulum Stars:
- ε Reticuli: An orange subgiant star of magnitude 4.44 around which an extrasolar planet orbits.
- ζ Reticuli: It is a binary system formed by two yellow dwarfs; the visual separation between them is 310 arcseconds. They are located 39.5 light-years from the Solar System.
- κ Reticuli: White-yellow star of magnitude 4.71.
- R Reticuli: It is a Mira variable star whose brightness ranges between 6.5 and 14.2 in 278.5 days.
- HD 23079: It is a yellow dwarf star distant 110 light-years that has an extrasolar planet.
- HD 23127: It is a yellow dwarf star where a planet has been discovered.
- HD 27894: It is an orange dwarf star with a planet.
Deep Sky Objects


Reticulum is also home to several deep-sky objects. Deep-sky objects often mean star clusters, nebulae (body of interstellar clouds), or galaxies.
In the case of Reticulum being a small constellation, it does not have many deep-sky objects, having only two notable galaxies.
Galaxy NGC 1313
It is a late barred spiral galaxy (SBd) with a small, bright core and a reasonably asymmetrical structure. It is in a transitional state between barred spiral galaxies (SB) and Magellanic irregular galaxies (Irr I).
It is the most notable deep sky object in the constellation Reticulum, with an apparent magnitude of +9.2. It also features strong radio wave emission and star formation in the regions with the highest surface brightness of its bars.
Galaxy NGC 1559
It is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Reticulum, with substantial spiral arms and strong star formation. It has a bar and disc, which are the source of powerful radio emissions.
Conclusions
- Reticulum is a constellation located primarily in the southern hemisphere. The name of the constellation comes from Latin and means "Recticula."
- Reticulum is one of the 88 modern constellations, so its name is not derived from a myth, history, or ancient legend like the most famous constellations.
- The constellation Reticulum lies between 23° N and 90° S. The best month to observe the constellation is January.
- The easiest way to locate the constellation Reticulum is to locate the star Canopus in the constellation Carina. Then we draw an imaginary straight line from Canopus to the star Achernar. The constellation Reticulum is located halfway between the two stars.
- The brightest star in the constellation Reticulum is Alpha Reticuli (α Ret / HD 27256 / HR 1336), with an apparent magnitude of +3.34.
- The most notable deep sky body in the constellation Reticulum is the galaxy NGC 1313.






